SpringBoot 指标监控actuator的专题
目录
- 1.写在前面
- 2.SpringBoot Actuator
- 3.定制化Endpoint
- 3.1 定制health端点信息
- 3.2 定制info端点信息
1.写在前面
首先肯定要说一下SpringBoot的四大核心了:
- 自动装配:简单配置甚至零配置即可运行项目
- 起步依赖:场景启动器
- Actuator:指标监控
- 命令行界面 :命令行
这篇文章呢,我来和大家聊聊指标监控这个东西。
2.SpringBoot Actuator
未来每一个微服务在云上部署以后,我们都需要对其进行监控、追踪、审计、控制等。SpringBoot就抽取了Actuator场景,使得我们每个微服务快速引用即可获得生产级别的应用监控、审计等功能。
要开启指标监控功能,首先需要在pom文件种添加如下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
然后在配置文件中先做如下配置:
server:
port: 8080
# 暴露所有监控信息为HTTP
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: true # 默认开启所有监控端点信息
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 以web方式暴露所有端点
然后启动项目,进行测试:
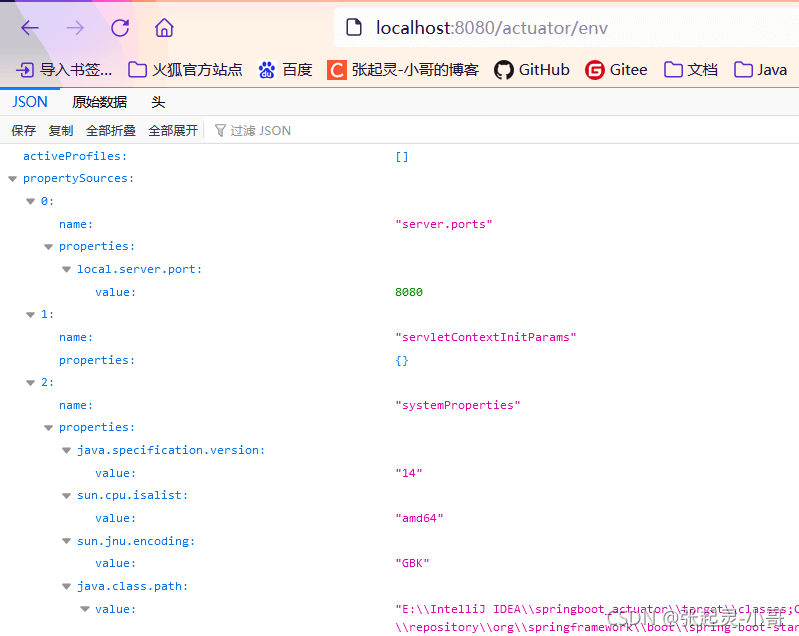
下图中测试得到的内容就是目前项目中可以监控到的各种指标参数信息。
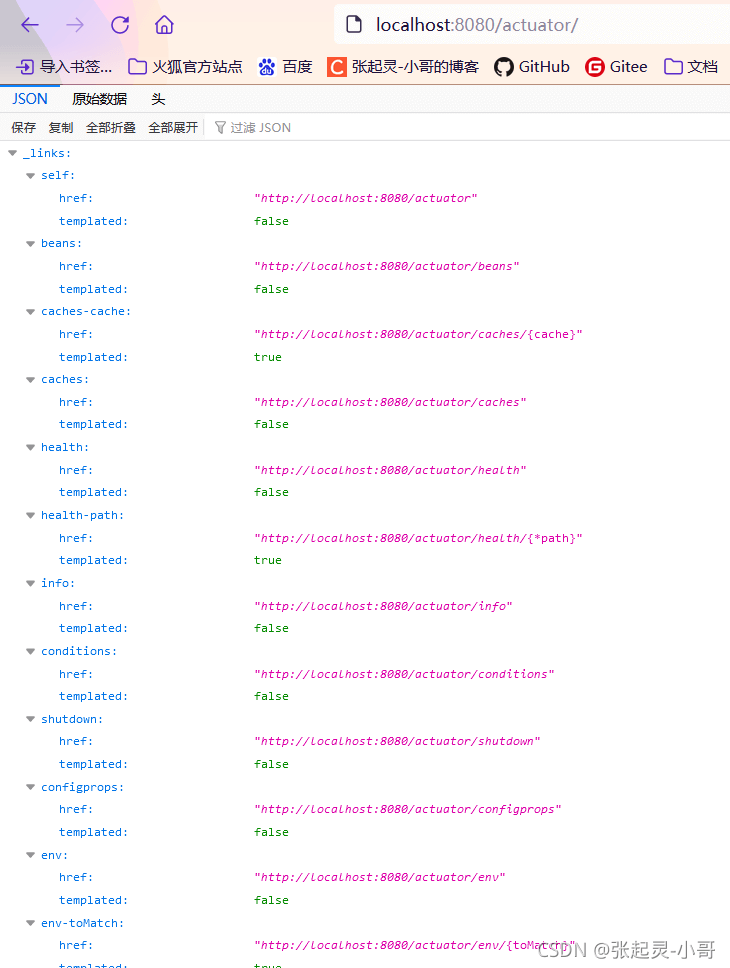
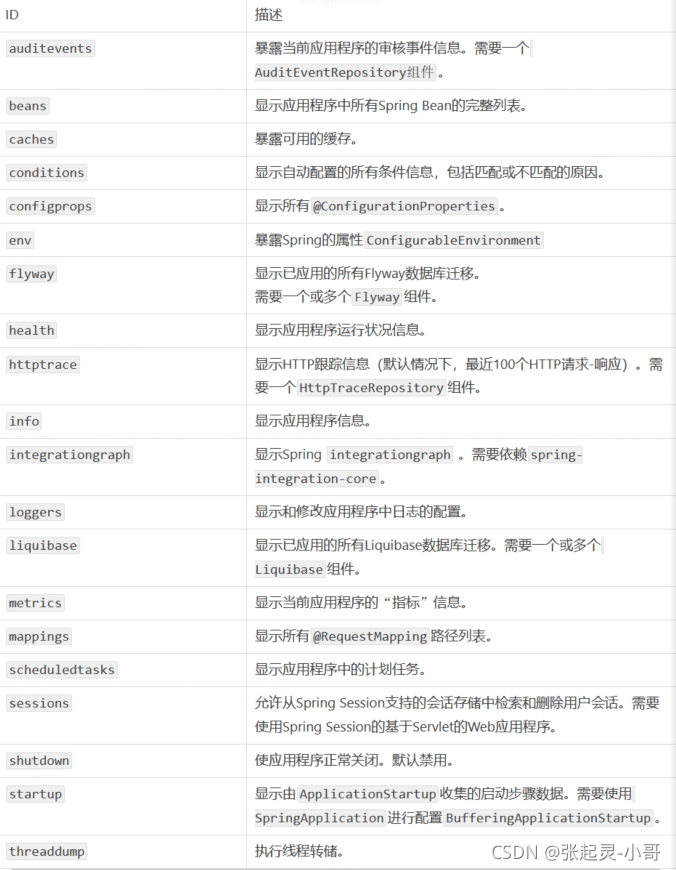
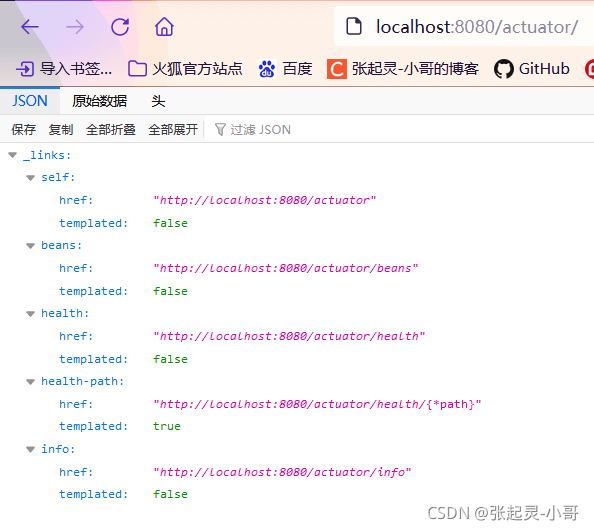
在指标监控这个功能中,有一个经常提到的词叫:端点。那么常用常见的端点如下图:👇👇👇
上面我们访问指标监控的url是:http://localhost:8080/actuator/ 即可获取到所有端点信息。那么如果想要获取某个端点信息,url就应该是:
http://localhost:8080/actuator/endpointName/detailPath。
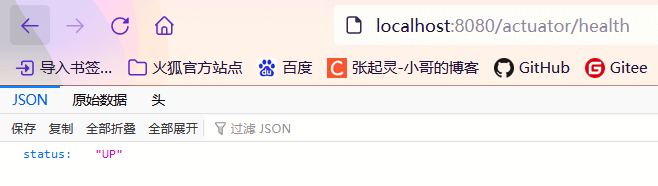
健康检查端点,我们一般用于在云平台,平台会定时的检查应用的健康状况,我们就需要Health Endpoint可以为平台返回当前应用的一系列组件健康状况的集合。
重要的几点:
- health endpoint返回的结果,应该是一系列健康检查后的一个汇总报告
- 很多的健康检查默认已经自动配置好了,比如:数据库、redis等
- 可以很容易的添加自定义的健康检查机制
提供详细的、层级的、空间指标信息,这些信息可以被pull(主动推送)或者push(被动获取)方式得到;
- 通过Metrics对接多种监控系统
- 简化核心Metrics开发
- 添加自定义Metrics或者扩展已有Metrics
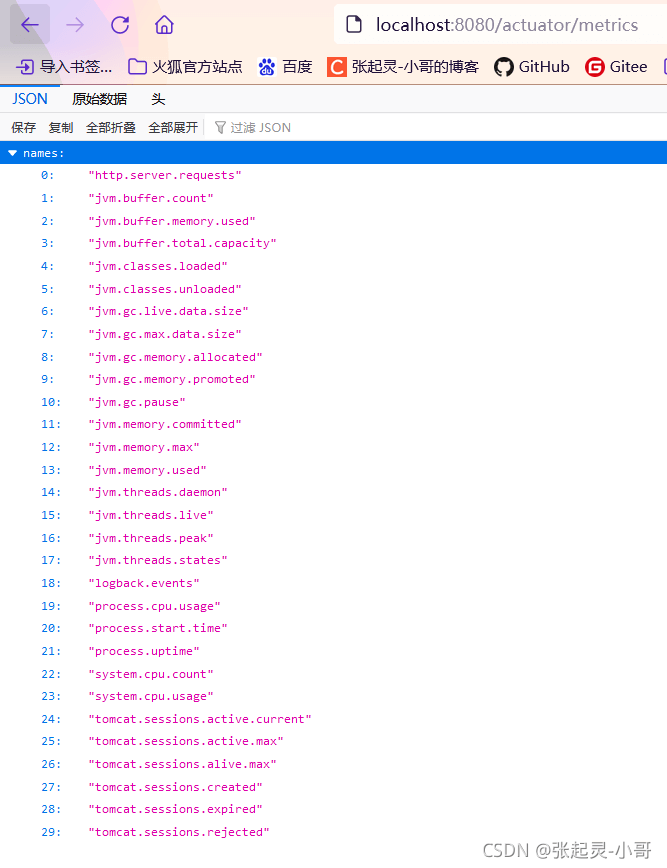
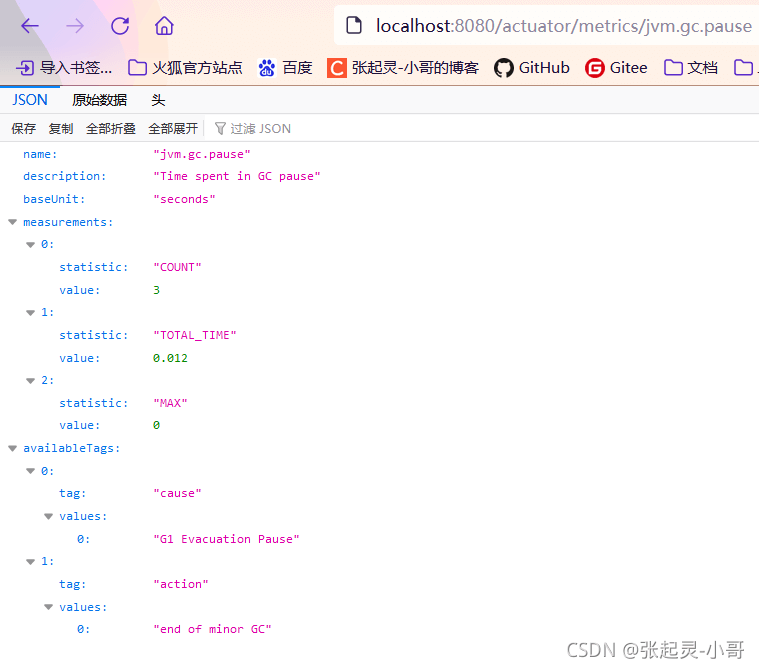
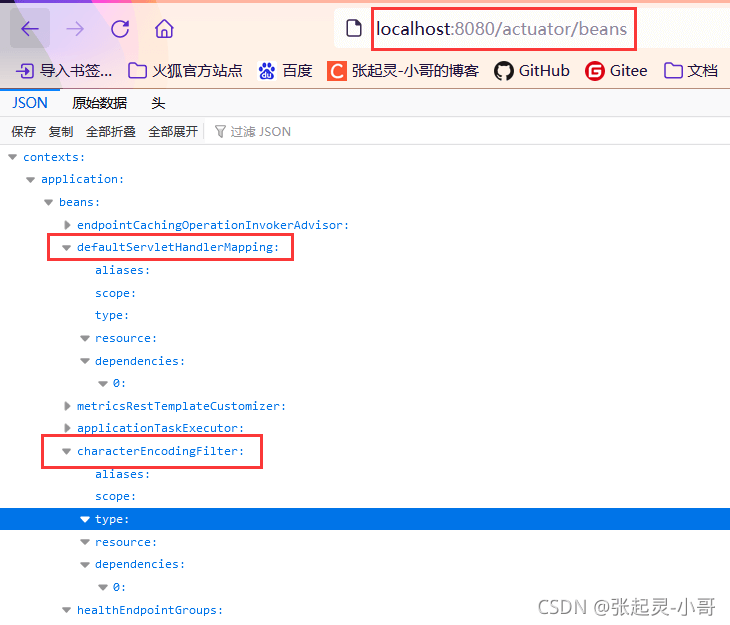
上面的这些测试结果就是我们根据当前项目,获取到某个端点的详细指标信息。
除此之外,我们也可以对这些端点进行手动开启或者禁用。(参见下面的配置文件)
server:
port: 8080
# 暴露所有监控信息为HTTP
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: false # 默认开启所有监控端点信息
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 以web方式暴露所有端点
# 需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint
# 配置模式为 management.endpoint.<endpointName>.enabled = true/false
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always # 总是显示health端点的详细信息
enabled: true
info:
enabled: true
beans:
enabled: true
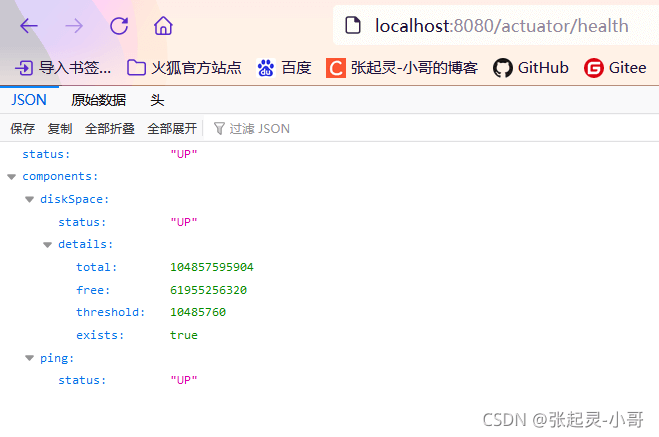
上面的测试截图就是我们手动的开启某些端点、同时关闭了某些端点之后的结果。
3.定制化Endpoint
3.1 定制health端点信息
以上的所有内容都是在使用SpringBoot为我们提供的官方的Endpoint,那么我们也是可以自定义Endpoint的(也即定制化Endpoint)。
有两种方式:①继承AbstractHealthIndicator抽象类(doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder)方法);②实现HealthIndicator接口(重写health()方法)。我是用第一种方法简单做个测试吧。
package com.szh.boot.health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.AbstractHealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Status;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
*
*/
@Component
public class MyComHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
/**
* 真实的检查方法
* @param builder
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//模拟检查过程
if (1 == 1) {
// builder.up(); //健康
builder.status(Status.UP);
map.put("count",1);
map.put("ms",100);
} else {
// builder.down(); //宕机
builder.status(Status.DOWN);
map.put("error","连接超时");
map.put("ms",3000);
}
builder.withDetail("code",20001)
.withDetails(map);
}
}
配置文件如下:👇👇👇
server:
port: 8080
# 暴露所有监控信息为HTTP
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: false # 默认开启所有监控端点信息
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 以web方式暴露所有端点
# 需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint
# 配置模式为 management.endpoint.<endpointName>.enabled = true/false
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always # 总是显示health端点的详细信息
enabled: true
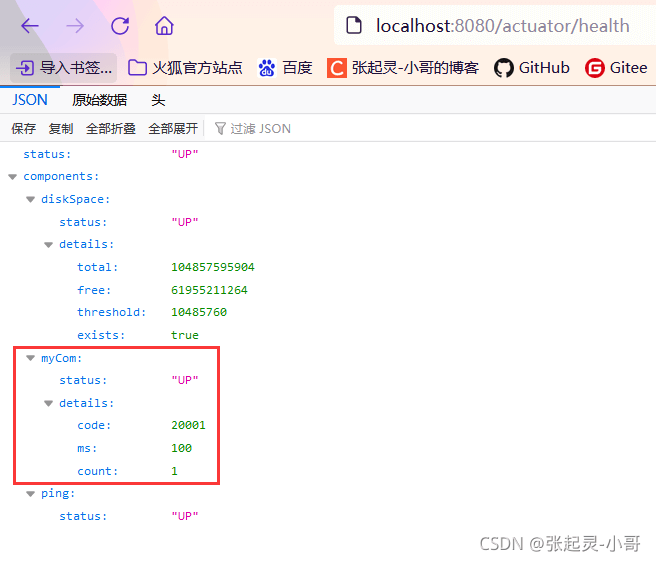
然后我们启动测试,访问路径:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health。从结果中看到有一个端点myCom就是我们自定义的(命名方式就是 MyComHealthIndicator 类去掉后面的 HealthIndicator)。
3.2 定制info端点信息
首先在配置文件中添加如下内容:(最后几行)
server:
port: 8080
# 暴露所有监控信息为HTTP
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: false # 默认开启所有监控端点信息
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 以web方式暴露所有端点
# 需要开启或者禁用某个Endpoint
# 配置模式为 management.endpoint.<endpointName>.enabled = true/false
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always # 总是显示health端点的详细信息
enabled: true
info:
enabled: true
beans:
enabled: true
info:
appName: spring-boot-actuator-endpoint-info
version: 2.0.0
mavenProjectName: @project.artifactId@
mavenProjectVersion: @project.version@
然后创建一个类,实现 InfoContributor 这个接口,并且重写接口中的 contribute(Info.Builder builder) 方法。
package com.szh.boot.info;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.info.Info;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.info.InfoContributor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
*
*/
@Component
public class ExampleInfoContributor implements InfoContributor {
@Override
public void contribute(Info.Builder builder) {
builder.withDetail("example", Collections.singletonMap("key","value"));
}
}
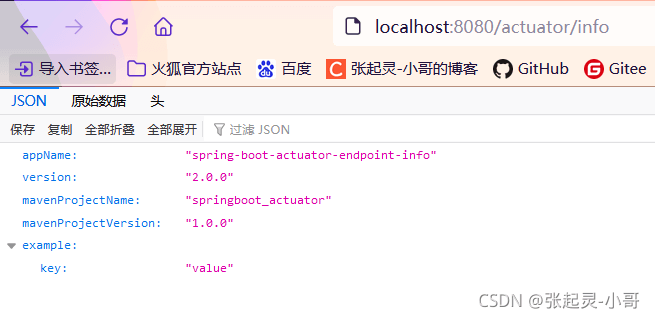
最后我们启动测试一下,访问路径:http://localhost:8080/actuator/info。得到的数据就是我们上面通过代码写好的内容。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot 指标监控actuator的专题的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot 指标监控内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
【文章转自:韩国cn2服务器 转载请保留连接】