python多进程登录远端服务器
目录
通过Semaphore 来控制对共享资源的的访问数量,可以控制同一时刻并发的进程数 。
#/usr/bin/python # _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_ import multiprocessing import time import paramiko def ssh(s,i,host):
try:
s.acquire()
print(time.strftime('%H:%M:%S'),multiprocessing.current_process().name + " 获得锁运行");
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect(hostname=host, port=22, username="root", password="yankefei")
print (host+" is login success")
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command("echo
d
a
t
e
&& df -hl")
print(stdout.read().decode('utf-8'))
returncode = stdout.channel.recv_exit_status()
print("returncode:",returncode)
except:
ssh.close()
# time.sleep(i)
print(time.strftime('%H:%M:%S'),multiprocessing.current_process().name + " 释放锁结束");
s.release()
print (host+" is unreachable")
finally:
ssh.close() s.release() if __name__ == "__main__": s = multiprocessing.Semaphore(200) #同时并发200个进程 for n in range(111): p = multiprocessing.Process(target = ssh, args=(s,2,"192.168.0."+str(n))) p.start()
运行结果如下图:
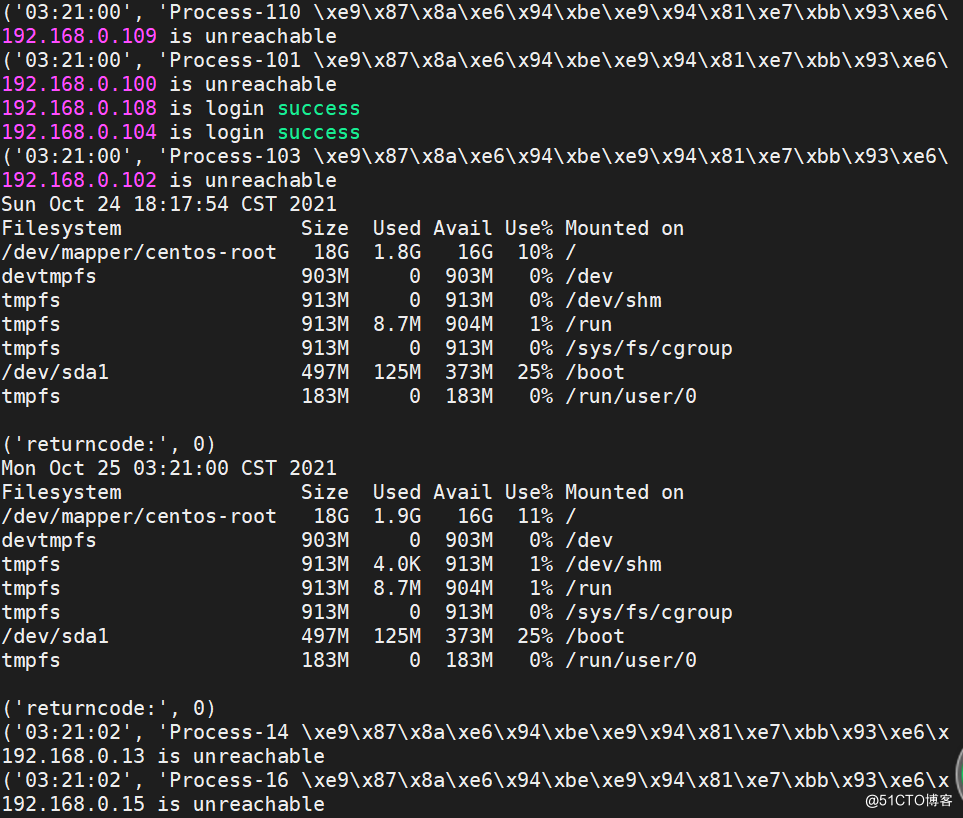
到此这篇关于python多进程登录远端服务器的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关多进程 Python内容请搜索hwidc以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持hwidc!
【文章转自:香港站群服务器 复制请保留原URL】