Python数学建模学习模拟退火算法旅行商问题示例
目录
- 1、旅行商问题(Travelling salesman problem, TSP)
- 2、模拟退火算法求解旅行商问题
- 3、 程序说明
- 4、模拟退火算法求解旅行商问题 Python 程序
- 5、运行结果
1、旅行商问题(Travelling salesman problem, TSP)
旅行商问题是经典的组合优化问题,要求找到遍历所有城市且每个城市只访问一次的最短旅行路线,即对给定的正权完全图求其总权重最小的Hamilton回路:设有 n个城市和距离矩阵 D=[dij],其中dij表示城市i到城市j的距离(i,j = 1,2 … n),则问题是要找出遍访每个城市恰好一次的一条回路并使其路径长度为最短。旅行商问题属于NP完全问题,其全局优化解的计算量以问题规模的阶乘关系增长。旅行商问题不仅作为一类典型的组合优化问题经常被用作算法研究和比较的案例,许多实际应用问题如路径规划、交通物流、网络管理也可转化为旅行商问题。
目前,旅行商问题的研究主要集中于探索和发展各种高效近似最优解的优化方法,包括基于问题特征信息(如城市位置、距离、角度等)构造的各种启发式搜索算法,以及通过模拟或解释自然规律而发展的模拟退火算法、遗传算法、蚁群算法、神经网络算法等智能优化算法或将二者相结合的混合算法。
2、模拟退火算法求解旅行商问题
模拟退火算法要从当前解的邻域中产生新的候选解,解的表达形式和邻域结构对算法收敛非常重要。组合优化问题不同于函数优化,其自变量不是连续变化的,目标函数不仅依赖于自变量的数值,而且与变量的排列次序有关。极端地,旅行商问题的路径长度仅取决于排列次序,因此常用城市编号的序列来表示解。
新解的产生机制是在当前解序列的基础上进行变换操作,随机改变序列中某些点的排列次序,常见的基本变换操作有交换算子(Swap Operator)、反序算子(Inversion Operator)、移位算子(Move Operator)等。交换算子将当前路径 S_now 中的第 i 个城市 Ci 与第 j 个城市 Cj 的位置交换;反序算子也称2-opt,将当前路径 S_now 中从第 i 个城市 Ci 到第 j 个城市 Cj 之间的城市排列顺序反向翻转;移位算子相当于 Or-opt 操作t,将当前路径 S_now 中的第 i 个城市 Ci 移动到第 j 个城市 Cj 之后的位置。
3、 程序说明
下段给出了模拟退火算法求解旅行商问题的 Python程序。对于程序中的一些细节处理,说明如下:
数据的获取。为了避免让读者下载数据文件,程序中采用直接赋值方式读取旅行城市位置的坐标。实际上,通常是使用数据文件给出城市位置的参数,程序中已经给出了读取 TSPLib(旅行商问题国际标准数据集)的子程序和调用方法。
城市间距的计算。按照 TSPLib 的处理规范,一是城市间距按欧式距离计算,不要说地球是圆的要算球面间距了;二是对计算的城市间距离取整(四舍五入),而不是用实数表示城市间距离,这会导致一些优化结果的差异。
新路径的产生。为便于理解,本程序只给出了交换算子(Swap Operator)的子程序。交换操作非常容易理解,但实际上优化效率和效果并不好,反序操作的性能显著优于交换算子。
4、模拟退火算法求解旅行商问题 Python 程序
# 模拟退火算法求解旅行商问题 Python程序
# Program: SimulatedAnnealing_v6.py
# Purpose: Simulated annealing algorithm for traveling salesman problem
# v1.0: = 关注 Youcans,分享原创系列 https://blog.csdn.net/youcans =
# 模拟退火求解旅行商问题(TSP)基本算法
# Copyright 2021 YouCans, XUPT
# Crated:2021-05-01
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import math # 导入模块 math
import random # 导入模块 random
import pandas as pd # 导入模块 pandas 并简写成 pd
import numpy as np # 导入模块 numpy 并简写成 np YouCans
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 导入模块 matplotlib.pyplot 并简写成 plt
np.set_printoptions(precision=4)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 20)
pd.set_option('expand_frame_repr', False)
pd.options.display.float_format = '{:,.2f}'.format
# 子程序:初始化模拟退火算法的控制参数
def initParameter():
# custom function initParameter():
# Initial parameter for simulated annealing algorithm
tInitial = 100.0 # 设定初始退火温度(initial temperature)
tFinal = 1 # 设定终止退火温度(stop temperature)
nMarkov = 1000 # Markov链长度,也即内循环运行次数
alfa = 0.98 # 设定降温参数,T(k)=alfa*T(k-1)
return tInitial,tFinal,alfa,nMarkov
# 子程序:读取TSPLib数据
def read_TSPLib(fileName):
# custom function read_TSPLib(fileName)
# Read datafile *.dat from TSPlib
# return coordinates of each city by YouCans, XUPT
res = []
with open(fileName, 'r') as fid:
for item in fid:
if len(item.strip())!=0:
res.append(item.split())
loadData = np.array(res).astype('int') # 数据格式:i Xi Yi
coordinates = loadData[:,1::]
return coordinates
# 子程序:计算各城市间的距离,得到距离矩阵
def getDistMat(nCities, coordinates):
# custom function getDistMat(nCities, coordinates):
# computer distance between each 2 Cities
distMat = np.zeros((nCities,nCities)) # 初始化距离矩阵
for i in range(nCities):
for j in range(i,nCities):
# np.linalg.norm 求向量的范数(默认求 二范数),得到 i、j 间的距离
distMat[i][j] = distMat[j][i] = round(np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i]-coordinates[j]))
return distMat # 城市间距离取整(四舍五入)
# 子程序:计算 TSP 路径长度
def calTourMileage(tourGiven, nCities, distMat):
# custom function caltourMileage(nCities, tour, distMat):
# to compute mileage of the given tour
mileageTour = distMat[tourGiven[nCities-1], tourGiven[0]] # dist((n-1),0)
for i in range(nCities-1): # dist(0,1),...dist((n-2)(n-1))
mileageTour += distMat[tourGiven[i], tourGiven[i+1]]
return round(mileageTour) # 路径总长度取整(四舍五入)
# 子程序:绘制 TSP 路径图
def plot_tour(tour, value, coordinates):
# custom function plot_tour(tour, nCities, coordinates)
num = len(tour)
x0, y0 = coordinates[tour[num - 1]]
x1, y1 = coordinates[tour[0]]
plt.scatter(int(x0), int(y0), s=15, c='r') # 绘制城市坐标点 C(n-1)
plt.plot([x1, x0], [y1, y0], c='b') # 绘制旅行路径 C(n-1)~C(0)
for i in range(num - 1):
x0, y0 = coordinates[tour[i]]
x1, y1 = coordinates[tour[i + 1]]
plt.scatter(int(x0), int(y0), s=15, c='r') # 绘制城市坐标点 C(i)
plt.plot([x1, x0], [y1, y0], c='b') # 绘制旅行路径 C(i)~C(i+1)
plt.xlabel("Total mileage of the tour:{:.1f}".format(value))
plt.title("Optimization tour of TSP{:d}".format(num)) # 设置图形标题
plt.show()
# 子程序:交换操作算子
def mutateSwap(tourGiven, nCities):
# custom function mutateSwap(nCities, tourNow)
# produce a mutation tour with 2-Swap operator
# swap the position of two Cities in the given tour
# 在 [0,n) 产生 2个不相等的随机整数 i,j
i = np.random.randint(nCities) # 产生第一个 [0,n) 区间内的随机整数
while True:
j = np.random.randint(nCities) # 产生一个 [0,n) 区间内的随机整数
if i!=j: break # 保证 i, j 不相等
tourSwap = tourGiven.copy() # 将给定路径复制给新路径 tourSwap
tourSwap[i],tourSwap[j] = tourGiven[j],tourGiven[i] # 交换 城市 i 和 j 的位置————简洁的实现方法
return tourSwap
def main():
# 主程序 = 关注 Youcans,分享原创系列 https://blog.csdn.net/youcans =
# # 读取旅行城市位置的坐标
coordinates = np.array([[565.0, 575.0], [25.0, 185.0], [345.0, 750.0], [945.0, 685.0], [845.0, 655.0],
[880.0, 660.0], [25.0, 230.0], [525.0, 1000.0], [580.0, 1175.0], [650.0, 1130.0],
[1605.0, 620.0], [1220.0, 580.0], [1465.0, 200.0], [1530.0, 5.0], [845.0, 680.0],
[725.0, 370.0], [145.0, 665.0], [415.0, 635.0], [510.0, 875.0], [560.0, 365.0],
[300.0, 465.0], [520.0, 585.0], [480.0, 415.0], [835.0, 625.0], [975.0, 580.0],
[1215.0, 245.0], [1320.0, 315.0], [1250.0, 400.0], [660.0, 180.0], [410.0, 250.0],
[420.0, 555.0], [575.0, 665.0], [1150.0, 1160.0], [700.0, 580.0], [685.0, 595.0],
[685.0, 610.0], [770.0, 610.0], [795.0, 645.0], [720.0, 635.0], [760.0, 650.0],
[475.0, 960.0], [95.0, 260.0], [875.0, 920.0], [700.0, 500.0], [555.0, 815.0],
[830.0, 485.0], [1170.0, 65.0], [830.0, 610.0], [605.0, 625.0], [595.0, 360.0],
[1340.0, 725.0], [1740.0, 245.0]])
# fileName = "../data/eil76.dat" # 数据文件的地址和文件名
# coordinates = read_TSPLib(fileName) # 调用子程序,读取城市坐标数据文件
# 模拟退火算法参数设置
tInitial,tFinal,alfa,nMarkov = initParameter() # 调用子程序,获得设置参数
nCities = coordinates.shape[0] # 根据输入的城市坐标 获得城市数量 nCities
distMat = getDistMat(nCities, coordinates) # 调用子程序,计算城市间距离矩阵
nMarkov = nCities # Markov链 的初值设置
tNow = tInitial # 初始化 当前温度(current temperature)
# 初始化准备
tourNow = np.arange(nCities) # 产生初始路径,返回一个初值为0、步长为1、长度为n 的排列
valueNow = calTourMileage(tourNow,nCities,distMat) # 计算当前路径的总长度 valueNow
tourBest = tourNow.copy() # 初始化最优路径,复制 tourNow
valueBest = valueNow # 初始化最优路径的总长度,复制 valueNow
recordBest = [] # 初始化 最优路径记录表
recordNow = [] # 初始化 最优路径记录表
# 开始模拟退火优化过程
iter = 0 # 外循环迭代次数计数器
while tNow >= tFinal: # 外循环,直到当前温度达到终止温度时结束
# 在当前温度下,进行充分次数(nMarkov)的状态转移以达到热平衡
for k in range(nMarkov): # 内循环,循环次数为Markov链长度
# 产生新解:
tourNew = mutateSwap(tourNow, nCities) # 通过 交换操作 产生新路径
valueNew = calTourMileage(tourNew,nCities,distMat) # 计算当前路径的总长度
deltaE = valueNew - valueNow
# 接受判别:按照 Metropolis 准则决定是否接受新解
if deltaE < 0: # 更优解:如果新解的目标函数好于当前解,则接受新解
accept = True
if valueNew < valueBest: # 如果新解的目标函数好于最优解,则将新解保存为最优解
tourBest[:] = tourNew[:]
valueBest = valueNew
else: # 容忍解:如果新解的目标函数比当前解差,则以一定概率接受新解
pAccept = math.exp(-deltaE/tNow) # 计算容忍解的状态迁移概率
if pAccept > random.random():
accept = True
else:
accept = False
# 保存新解
if accept == True: # 如果接受新解,则将新解保存为当前解
tourNow[:] = tourNew[:]
valueNow = valueNew
# 平移当前路径,以解决变换操作避开 0,(n-1)所带来的问题,并未实质性改变当前路径。
tourNow = np.roll(tourNow,2) # 循环移位函数,沿指定轴滚动数组元素
# 完成当前温度的搜索,保存数据和输出
recordBest.append(valueBest) # 将本次温度下的最优路径长度追加到 最优路径记录表
recordNow.append(valueNow) # 将当前路径长度追加到 当前路径记录表
print('i:{}, t(i):{:.2f}, valueNow:{:.1f}, valueBest:{:.1f}'.format(iter,tNow,valueNow,valueBest))
# 缓慢降温至新的温度,
iter = iter + 1
tNow = tNow * alfa # 指数降温曲线:T(k)=alfa*T(k-1)
# 结束模拟退火过程
# 图形化显示优化结果
figure1 = plt.figure() # 创建图形窗口 1
plot_tour(tourBest, valueBest, coordinates)
figure2 = plt.figure() # 创建图形窗口 2
plt.title("Optimization result of TSP{:d}".format(nCities)) # 设置图形标题
plt.plot(np.array(recordBest),'b-', label='Best') # 绘制 recordBest曲线
plt.plot(np.array(recordNow),'g-', label='Now') # 绘制 recordNow曲线
plt.xlabel("iter") # 设置 x轴标注
plt.ylabel("mileage of tour") # 设置 y轴标注
plt.legend() # 显示图例
plt.show()
print("Tour verification successful!")
print("Best tour: \n", tourBest)
print("Best value: {:.1f}".format(valueBest))
exit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
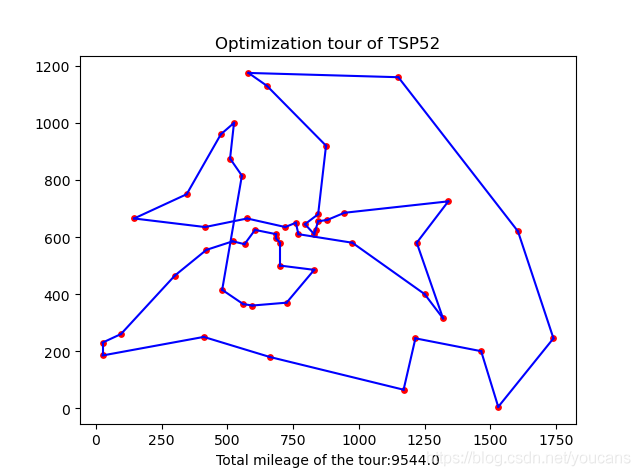
5、运行结果
程序的运行结果只供参考,显然这并不是最优结果。
Tour verification successful! Best tour: [18 7 40 2 16 17 31 38 39 36 24 27 26 11 50 3 5 4 23 47 37 14 42 9 8 32 10 51 13 12 25 46 28 29 1 6 41 20 30 21 0 48 35 34 33 43 45 15 49 19 22 44] Best value: 9544.0
以上就是Python数学建模学习模拟退火算法旅行商问题示例解析的详细内容,更多关于数学建模模拟退火算法的资料请关注hwidc其它相关文章!
【本文来源:bgp服务器 欢迎转载】