Java SpringCache+Redis缓存数据详解
目录
- 前言
- 一、什么是SpringCache
- 二、项目集成Spring Cache + Redis
- 1、配置方式
- 三、使用Spring Cache
- 四、SpringCache原理与不足
- 1、读模式
- 2、写模式:(缓存与数据库一致)
- 五、总结
前言
这几天学习谷粒商城又再次的回顾了一次SpringCache,之前在学习谷粒学院的时候其实已经学习了一次了!!!
这里就对自己学过来的内容进行一次的总结和归纳!!!
一、什么是SpringCache
- Spring Cache 是一个非常优秀的缓存组件。自Spring 3.1起,提供了类似于@Transactional注解事务的注解Cache支持,且提供了Cache抽象,方便切换各种底层Cache(如:redis)
- 使用Spring Cache的好处:
- 提供基本的Cache抽象,方便切换各种底层Cache;
- 通过注解Cache可以实现类似于事务一样,缓存逻辑透明的应用到我们的业务代码上,且只需要更少的代码就可以完成;
- 提供事务回滚时也自动回滚缓存;
- 支持比较复杂的缓存逻辑;
二、项目集成Spring Cache + Redis
- 依赖
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
开启@EnableCaching
1、配置方式
①第一种:配置类
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* 自定义key规则
* @return
*/
@Bean
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
sb.append(method.getName());
for (Object obj : params) {
sb.append(obj.toString());
}
return sb.toString();
}
};
}
/**
* 设置RedisTemplate规则
* @param redisConnectionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
// 指定要序列化的域,field,get和set,以及修饰符范围,ANY是都有包括private和public
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
// 指定序列化输入的类型,类必须是非final修饰的,final修饰的类,比如String,Integer等会跑出异常
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
//序列号key value
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 设置CacheManager缓存规则
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题),过期时间600秒
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
或
②结合配置+配置文件
spring:
cache:
#指定缓存类型为redis
type: redis
redis:
# 指定redis中的过期时间为1h
time-to-live: 3600000
key-prefix: CACHE_ #缓存key前缀
use-key-prefix: true #是否开启缓存key前缀
cache-null-values: true #缓存空值,解决缓存穿透问题
默认使用jdk进行序列化(可读性差),默认ttl为-1永不过期,自定义序列化方式为JSON需要编写配置类
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)//拿到Redis在配置文件的配置
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {
//获取到配置文件中的配置信息
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis(); org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration config = org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
//指定缓存序列化方式为json
config = config.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
//设置配置文件中的各项配置,如过期时间
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
说明:
第一种,全自定义配置第二种,简单配置+自定义配置value值json转义
- 对redis进行配置
#redis配置 spring.redis.host=47.120.237.184 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password=ach2ng@123356 spring.redis.database= 0 spring.redis.timeout=1800000 #redis池设置 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=20 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1 #最大阻塞等待时间(负数表示没限制) spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=5 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
三、使用Spring Cache
@Cacheable
根据方法对其返回结果进行缓存,下次请求时,如果缓存存在,则直接读取缓存数据返回;如果缓存不存在,则执行方法,并把返回的结果存入缓存中。一般用在查询方法上。
{"catagory","xxxx",....}#root.methodName【用方法名作为key】避免缓存击穿问题@CachePut
使用该注解标志的方法,每次都会执行,并将结果存入指定的缓存中。其他方法可以直接从响应的缓存中读取缓存数据,而不需要再去查询数据库。一般用在新增方法上。
{"catagory","xxxx",....}@CacheEvict
使用该注解标志的方法,会清空指定的缓存。一般用在更新或者删除方法上
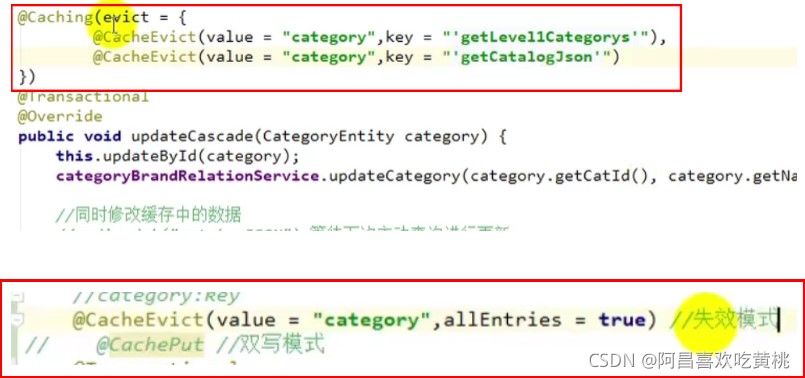
{"catagory","xxxx",....}@Caching
可组合使用以上注解,如:
//组合了删除缓存的@CacheEvict注解,同时删除两个
@Cacheing(evict=
{@CacheEvict(value="a"),key="'getLists'"}),
{@CacheEvict(value="b"),key="'getArr'"})
)
使用举例 失效模式: 更新操作后,删除缓存 双写模式: 更新操作后,新增缓存,掩盖
四、SpringCache原理与不足
1、读模式
缓存穿透:
查询一个null数据。
解决方案:缓存空数据
可通过spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values=true
缓存击穿:
大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据。
解决方案: 加锁 ? 默认是无加锁的;
使用sync = true来解决击穿问题
缓存雪崩:
大量的key同时过期。
解决方案:加随机时间,time-to-live: 3600000。
2、写模式:(缓存与数据库一致)
- 读写加锁。
- 引入Canal,感知到MySQL的更新去更新Redis
- 读多写多,直接去数据库查询就行
五、总结
常规数据(读多写少,即时性,一致性要求不高的数据,完全可以使用Spring-Cache):
写模式(只要缓存的数据有过期时间就足够了)
特殊数据:
特殊设计(读写锁、redis分布锁等
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注自由互联的更多内容!
【本文由:香港云服务器http://www.558cloud.com提供,感谢】