C++ 基于BFS算法的走迷宫自动寻路的实现
目录
- 1.效果图
- 2.实现代码
- 1.队列方法类
- 2.地图方法类
- 3.main函数
- 3.思路
1.效果图
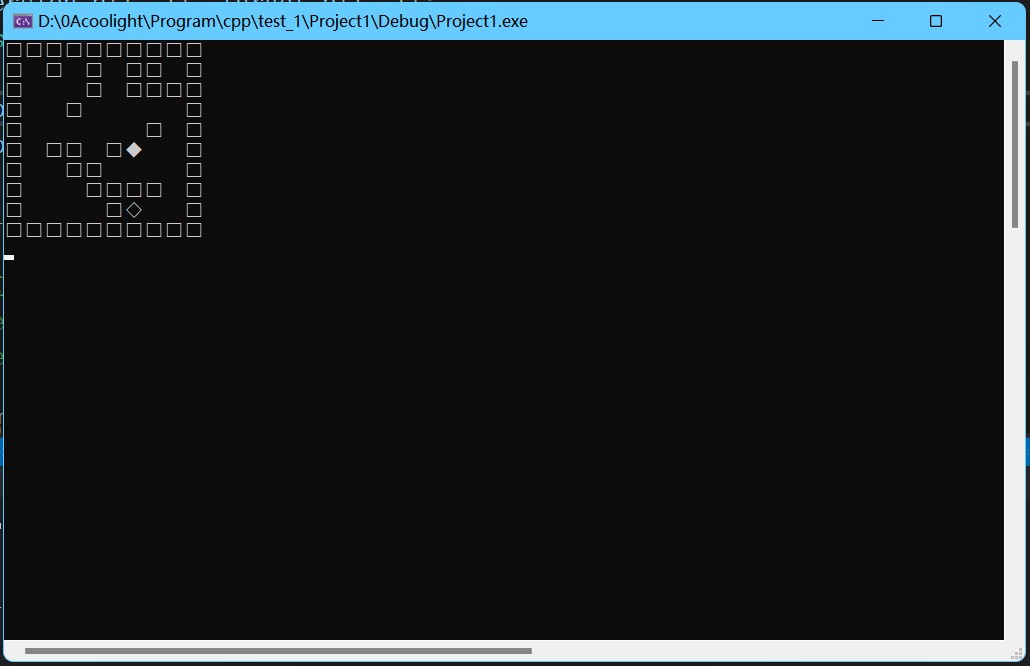
其中正方形代表障碍物,实心菱形代表移动者(人),空心菱形代表目标位置(都是可以在代码中修改的)
本例使用队列(链表实现),以广度优先进行自动寻路。
2.实现代码
1.队列方法类
coolQueue.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//队列
//坐标结构体
struct Point
{
int x;
int y;
Point()
{
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point(int in_x, int in_y)
{
x = in_x;
y = in_y;
}
Point& operator=(const Point& right_p)
{
this->x = right_p.x;
this->y = right_p.y;
return *this;
}
};
//队列结构体
struct coolQueue
{
int data;
Point cool_p;
coolQueue* next_p;
coolQueue(int in_data)
{
data = in_data;
next_p = NULL;
}
coolQueue(int in_x, int in_y, int in_data = 0)
{
cool_p.x = in_x;
cool_p.y = in_y;
data = in_data;
next_p = NULL;
}
};
//队列方法类,限制访问方式
class queueClass
{
protected:
coolQueue* Head_p = NULL;
coolQueue* End_p = NULL;
public:
queueClass() {}
void push(int data); //入队
void push(int in_x, int in_y, int in_data = 0);
bool pop(int& re_data); //出队
bool pop(coolQueue& in_coolQueue);
void reverse_order(); //翻转
void clear()
{
for (int data; pop(data););
}
~queueClass()
{
clear();
}
};
coolQueue.cpp
#include "coolQueue.h"
/*入队函数
* 传参:
* in_data:入队的数据
*/
void queueClass::push(int in_data)
{
if (Head_p == NULL) //队列为空
{
Head_p = new coolQueue(in_data);
End_p = Head_p;
}
else if(Head_p == End_p) //队列只有一个元素
{
End_p = new coolQueue(in_data);
Head_p->next_p = End_p;
}
else
{
coolQueue* temp_p = new coolQueue(in_data);
End_p->next_p = temp_p;
End_p = temp_p;
}
}
/*出队
* 传参:
* re_data:接收出队返回值
* 返回值:
* 成功返回true,队列为空返回false
*
* 把值写入re_data中返回
*/
bool queueClass::pop(int& re_data)
{
if (Head_p == NULL) //队列为空
return false;
re_data = Head_p->data;
coolQueue* temp_p = Head_p;
if (Head_p == End_p) //队列只有一个元素
{
Head_p = NULL;
End_p = NULL;
}
else
Head_p = Head_p->next_p;
delete temp_p;
return true;
}
/*同链表采用以尾指针为头的头插法实现倒序
*/
void queueClass::reverse_order()
{
if (Head_p == NULL || Head_p == End_p)
return;
coolQueue* p = Head_p, * temp_p;
do {
temp_p = p;
p = p->next_p;
temp_p->next_p = End_p->next_p;
End_p->next_p = temp_p;
} while (p != End_p);
p = Head_p;
Head_p = End_p;
End_p = p;
}
//以下重载用于辅助自动寻路实现
//in_data = 0
void queueClass::push(int in_x, int in_y, int in_data)
{
if (Head_p == NULL)
{
Head_p = new coolQueue(in_x, in_y, in_data);
End_p = Head_p;
}
else if (Head_p == End_p)
{
End_p = new coolQueue(in_x, in_y, in_data);
Head_p->next_p = End_p;
}
else
{
coolQueue* temp_p = new coolQueue(in_x, in_y, in_data);
End_p->next_p = temp_p;
End_p = temp_p;
}
}
bool queueClass::pop(coolQueue& in_coolQueue)
{
if (Head_p == NULL)
return false;
in_coolQueue.data = Head_p->data; //不直接使用复制是因为可能把Head_p的next_p也复制出去导致限制访问权限失效
in_coolQueue.cool_p = Head_p->cool_p;
coolQueue* temp_p = Head_p;
if (Head_p == End_p)
{
Head_p = NULL;
End_p = NULL;
}
else
Head_p = Head_p->next_p;
delete temp_p;
return true;
}
2.地图方法类
mapClass.h
#pragma once
#include "coolQueue.h"
#include "windows.h"
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#ifndef PI
#define PI 3.14159265358979323846
#endif // !PI
#ifndef Sleep_num
#define Sleep_num 500
#endif // !打印输出地图时的暂停时间
#ifndef Map_size
#define Map_size 10
#endif // !地图大小
/*地图操作类
* 保护继承队列,防止外部调用队列的函数
*/
class mapClass : protected queueClass
{
protected:
int map[Map_size][Map_size]; //地图
Point persion_p; //起点位置坐标
void new_map();
void reflash_map();
bool auto_find_way(Point& target_p);
void auto_move(int in_x, int in_y);
public:
mapClass(const Point& in_p);
bool auto_main();
void into_map(int in_data, int num = 1);
bool into_map(int in_x, int in_y, int in_data);
void show_map();
void clear_map(const Point& in_p);
};
mapClass.cpp
#include "mapClass.h"
/*初始化地图
*
* 把map置零后设置边界
*/
void mapClass::new_map()
{
memset(map, 0, Map_size * Map_size);//清零
for (int num = Map_size; num--;) //设置边缘障碍物
{
map[num][0] = 1;
map[0][num] = 1;
map[num][Map_size - 1] = 1;
map[Map_size - 1][num] = 1;
}
}
/*刷新地图
*
* 由于在auto_find_way()中会修改地图中的值作为方向标记
* 移动后会残留一些标记,此函数将会把这些标记清理(即把标记置回0)
*/
void mapClass::reflash_map()
{
for (int x = Map_size - 1; --x;)
for (int y = Map_size - 1; --y;)
map[x][y] = map[x][y] % 1000;
/*方向标记为1000,2000,3000 和 4000,故 %1000 即可保留其他东西并清理标记*/
}
/*自动寻路
*
* 传参:
* &target_p:传出参数,找到路径后写入目标的坐标
* 返回值:
* 有路径返回true,没有返回false
*
* 基于队列寻找到达目标的最优路径,会在地图上留下方向标记
* 如果找到,在其他函数可以 以目标位置开始,通过方向标记倒推回起点,即为路径
*/
bool mapClass::auto_find_way(Point& target_p)
{
coolQueue out_queue(0, 0, 0);
for (int push_num = 1; push_num;)
{
push_num = 0; //如果push_num在while循环后仍然为0,说明队列空且无路可走了
while (this->pop(out_queue))
{
for (int i = 1, temp_x, temp_y; i <= 4; ++i)//判断它的旁边4个位置
{ //此处使用sin()是为了在不同i时(temp_x, temp_y)指向以out_queue为中心的不同方向
//效果同auto_move()中的switch()的使用
temp_x = out_queue.cool_p.x + int(sin(PI / 2 * (i - 2.0)));
temp_y = out_queue.cool_p.y + int(sin(PI / 2 * (i - 3.0)));
switch (map[temp_x][temp_y])
{
case 0: //可走
{
map[temp_x][temp_y] = i * 1000; //写入方向标记
this->push(temp_x, temp_y, 0); //入队
++push_num;
}break;
case 10: //抵达目标位置
{
map[temp_x][temp_y] += i * 1000;
target_p.x = temp_x; //写入目标位置
target_p.y = temp_y;
this->clear(); //清空队列
return true;
}break;
}
}
if (out_queue.data == -1) //每一轮队列的最后一个的data标记为-1
break; //以起点位置往外一步为一轮
}
if (this->End_p != NULL)
this->End_p->data = -1;
}
this->clear();
return false;
}
/*自动移动(递归函数)
* 传参:
*
* 后序递归:先调用递归,再移动地点
* 因此此函数目的是一开始传入目标位置,
* 再以地图上的方向标记倒推上一个位置,
* 直到回到起点位置则开始移动,每次移动调用show()刷新地图显示
* 即可实现从起点到终点移动的效果
*/
void mapClass::auto_move(int in_x, int in_y)
{
/*switch ()可替换为
* temp_x = in_x + int(sin(PI / 2 * (map[in_x][in_y] / 1000));
* temp_y = in_y + int(sin(PI / 2 * (map[in_x][in_y] / 1000 - 1.0));
*/
int temp_x = in_x, temp_y = in_y;
switch (map[in_x][in_y] / 1000) //解析地图标记
{
case 0:return; break;
case 1:++temp_x; break;
case 2:++temp_y; break;
case 3:--temp_x; break;
case 4:--temp_y; break;
}
/*由于函数是从终点位置递归回起点的,所以上一个调用此函数的应该是更接近终点的
* 因此此函数接受的传入值(in_x, in_y)是下一个移动点
* (temp_x,temp_y)为本次的移动点
*/
auto_move(temp_x, temp_y); //递归调用,让起点移动到本位置(即temp_x, temp_y)
map[temp_x][temp_y] = 0; //把现在的位置清零
map[in_x][in_y] = 100; //把下一个移动点置100,即可实现从现在的位置移动到下一个位置的效果
show_map(); //显示打印
Sleep(Sleep_num);
return;
}
/*构造函数
* 传参:
* in_p:起点位置
*/
mapClass::mapClass(const Point& in_p)
{
new_map();
persion_p = in_p;
}
/*自动寻路主导函数
*/
bool mapClass::auto_main()
{
show_map(); //显示地图
Sleep(Sleep_num);
this->clear(); //清空队列
this->push(persion_p.x, persion_p.y, -1);//把起点入队
Point target_p; //目标坐标
if (auto_find_way(target_p) == false) //调用自动寻路
{
reflash_map();
return false;
}
auto_move(target_p.x, target_p.y); //移动
reflash_map(); //清理地图残留标记
persion_p = target_p; //重置起点位置,抵达终点后起点即为终点
return true;
}
/*对地图写入数据标记
*
* 传参:
* in_data:写入的数据值
* num: 次数
*
* 在地图的随机空位置上写入 num 次 in_data 标记
*
* 存在bug:
* 如果地图坐标已满,写入次数不够会陷入死循环
* 可考虑加入循环次数限制解决
*/
void mapClass::into_map(int in_data, int num)
{
if (num <= 0)
return;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; num--;)
{
i = rand() % Map_size;
j = rand() % Map_size;
if (map[i][j] == 0)
map[i][j] = in_data;
else
++num;
}
}
/*对地图写入数据标记
*
* 传参:
* in_x,in_y:写入的地图位置
* in_data: 写入的数据值
*
* 返回值:
* 如果(in_x, in_y)位置为空则写入成功返回true,否则返回false
*
* 在地图的(in_x, in_y)位置写入 in_data
*/
bool mapClass::into_map(int in_x, int in_y, int in_data)
{
if (map[in_x][in_y] == 0)
{
map[in_x][in_y] = in_data;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*打印显示地图
*/
void mapClass::show_map()
{
system("cls"); //清空控制台输出
for (int i = 0; i < Map_size; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Map_size; ++j)
switch (map[i][j] % 1000)
{
case 0: cout << " "; break;//空白位置
case 1: cout << "□"; break;//障碍物
case 10: cout << "◇"; break;//目标
case 100: cout << "◆"; break;//自己
default: cout << " "; break;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
/*重置地图
* 传参:
* in_p:起点位置
*
* 清空地图,仅保留 起点 和 边界 标记
* 用于辅助循环刷新障碍物寻路的实现
*/
void mapClass::clear_map(const Point& in_p)
{
for (int x = Map_size - 1; --x;) //把地图中的所有位置置零
for (int y = Map_size - 1; --y;)
map[x][y] = 0;
persion_p = in_p; //重新设置起点
map[in_p.x][in_p.y] = 100;
}
3.main函数
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <cmath>
#include "mapClass.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(int(time(0)));
Point persion_p(1, 1), target_p(1, 1);
mapClass test_map(persion_p);
test_map.into_map(1, 1, 100); //写入起点
test_map.into_map(1, 20); //写入障碍物
while (1)
{
//重置障碍物位置, 取消下面两句的注释即可启用
//test_map.clear_map(target_p); //清空地图
//test_map.into_map(1, 20); //生成障碍物
do {
target_p.x = rand() % (Map_size - 2) + 1;
target_p.y = rand() % (Map_size - 2) + 1;
} while (test_map.into_map(target_p.x, target_p.y, 10) == false);
if (test_map.auto_main() == false)
{
cout << endl << "<< 走不了!" << endl;
Sleep(1500);
}
}
return 0;
}
3.思路
总体和数据结构的教科书上的大差不差:以起点为中心,每向外一步作为一轮循环,循环中把可走的位置入队,下一轮循环把上一轮入队的位置出队并再以这些位置为中心往外走一步,把可走位置入队,一直这样循环,直到遇到终点位置或者队列中为空(因为每一个方向都走不了则队列循环后为空)。
(想象一下在没有障碍物的地图中,以起点为中心向外扩散)
在上述过程中,把可走位置入队的同时留下方向标记(上一个位置走到此位置的方向),在循环结束后从终点位置倒推即可找到一条回到起点的路径。
此路径为最优解(最优解可能不止一条),因为算法中是从起点往外每一步进行一轮判断,因此如果找到了终点,那么就是在最少的步数内找到了终点,此时即可结束循环,此为最优解。如果不结束,继续找下去可能可以找到用更多步数的路径。
本例与书中的不同:
1.在找到路径后利用system("cls")清屏重新输出,来实现逐步走向终点的效果。
2.在一些细节的实现上使用不同的尝试(例如 mapClass::auto_find_way()中使用sin(),直接使用地图做方向标记等)
3.支持循环多次寻路,支持重置障碍物位置
到此这篇关于C++ 基于BFS算法的走迷宫自动寻路的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ 内容请搜索海外IDC网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持海外IDC网!
【文章出处:香港多ip服务器 复制请保留原URL】