OpenCV和C++实现图像的翻转(镜像)、平移、旋转
目录
- 一、翻转(镜像)
- 二、仿射扭曲
- 获取变换矩阵
- 仿射扭曲函数 warpAffine
- 旋转
- 平移
- 三、仿射变换
- 四、透视变换
- 综合示例
- 总结
官网教程
一、翻转(镜像)
头文件 quick_opencv.h:声明类与公共函数
#pragma once
#include <opencv2\opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
class QuickDemo {
public:
...
void flip_Demo(Mat& image);
void rotate_Demo(Mat& image);
void move_Demo(Mat& image);
void Affine_Demo(Mat& image);
void toushi_Demo(Mat& image);
void perspective_detect(Mat& image);
};
主函数调用该类的公共成员函数
#include <opencv2\opencv.hpp>
#include <quick_opencv.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
Mat src = imread("D:\\Desktop\\pandas.jpg");
if (src.empty()) {
printf("Could not load images...\n");
return -1;
}
namedWindow("input", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("input", src);
QuickDemo qk;
...
qk.Affine_Demo(src);
qk.move_Demo(src);
qk.flip_Demo(src);
qk.toushi_Demo(src);
qk.perspective_detect(src);
waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
源文件 quick_demo.cpp:实现类与公共函数
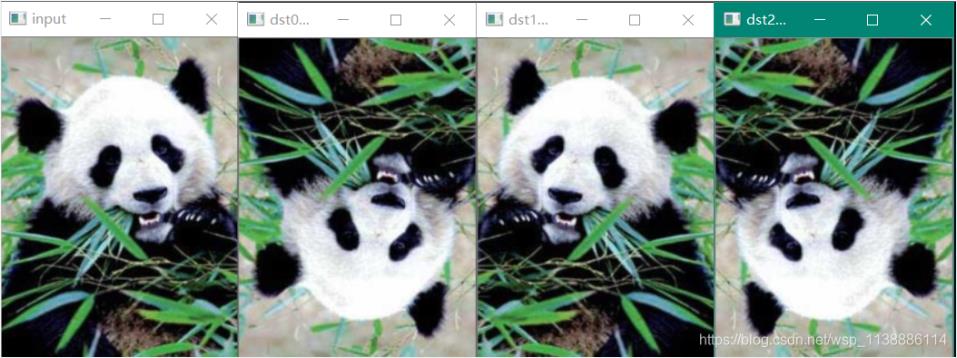
void QuickDemo::flip_Demo(Mat& image) {
Mat dst0, dst1, dst2;
flip(image, dst0, 0);
flip(image, dst1, 1);
flip(image, dst2, -1);
imshow("dst0_上下翻转", dst0);
imshow("dst1_左右翻转", dst1);
imshow("dst2_对角线翻转", dst2); //旋转180度
}
二、仿射扭曲
二维图像一般情况下的变换矩阵(旋转+平移),当我们只需要平移的时候,取 θ 的值为0,a和b的值就代表了图像沿x轴和y轴移动的距离;其中原图  (原图大小,不执行缩放)
(原图大小,不执行缩放)
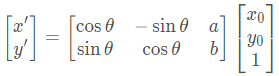
获取变换矩阵
变换矩阵计算:

其中: 
Mat getRotationMatrix2D( Point2f center, 源图像中旋转的中心
double angle, 角度以度为单位的旋转角度。正值表示逆时针旋转(坐标原点假定为左上角)。
double scale 各向同性比例因子。
)
仿射扭曲函数 warpAffine
函数签名
void warpAffine( InputArray src, 输入矩阵
OutputArray dst, 输出矩阵
InputArray M, 2×3 变换矩阵
Size dsize, 输出图像大小
int flags = INTER_LINEAR, 插值方式:默认线性插值
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, 边缘处理方式
const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar() 边缘填充值,默认=0
);
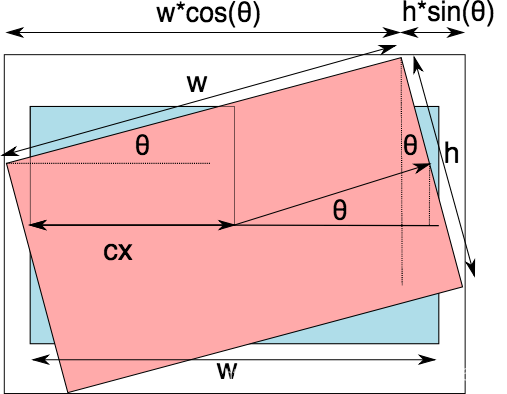
保留所有原图像素的旋转,原理: 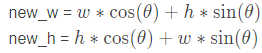
旋转
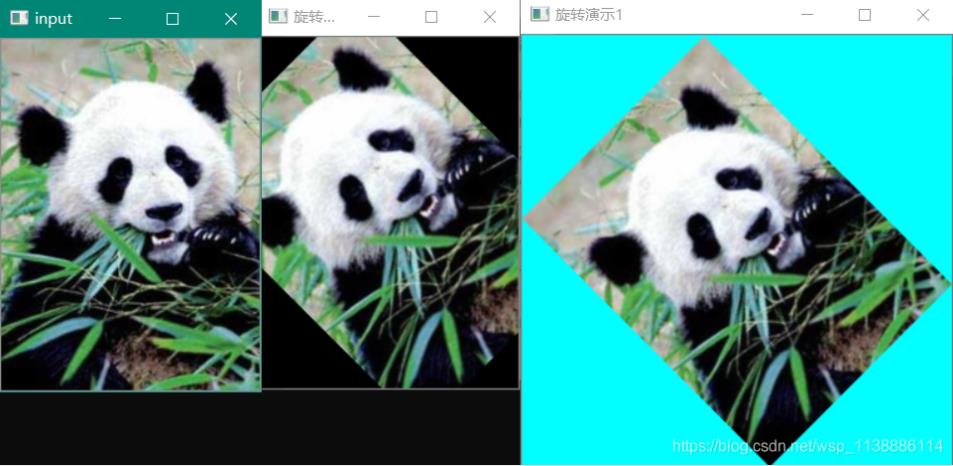
void QuickDemo::rotate_Demo(Mat& image) {
Mat dst_0, dst_1, M;
int h = image.rows;
int w = image.cols;
M = getRotationMatrix2D(Point(w / 2, h / 2), 45, 1.0);
warpAffine(image, dst_0, M, image.size());
double cos = abs(M.at<double>(0, 0));
double sin = abs(M.at<double>(0, 1));
int new_w = cos * w + sin * h;
int new_h = cos * h + sin * w;
M.at<double>(0, 2) += (new_w / 2.0 - w / 2);
M.at<double>(1, 2) += (new_h / 2.0 - h / 2);
warpAffine(image, dst_1, M, Size(new_w, new_h), INTER_LINEAR, 0, Scalar(255, 255, 0));
imshow("旋转演示0", dst_0);
imshow("旋转演示1", dst_1);
}
依次为:原图,旋转45度,保留所有原图像素的旋转45度
平移
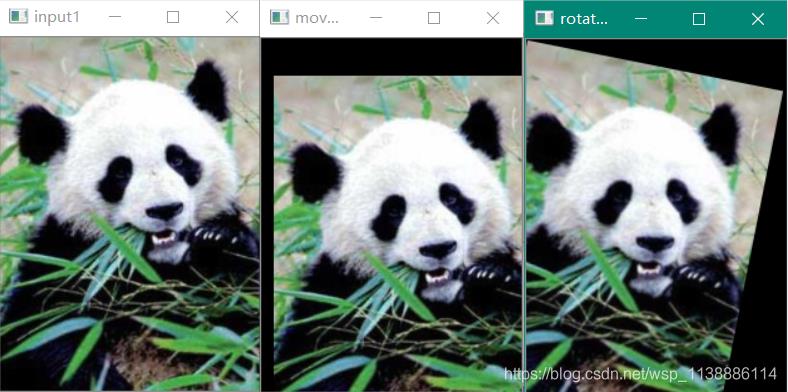
void QuickDemo::move_Demo(Mat& image) {
Mat dst_move;
Mat move_mat = (Mat_<double>(2, 3) << 1, 0, 10, 0, 1, 30);//沿x轴移动10沿y轴移动30
warpAffine(image, dst_move, move_mat, image.size());
imshow("dst_move", dst_move);
double angle_ = 3.14159265354 / 16.0;
cout << "pi=" << cos(angle_) << endl;
Mat rota_mat = (Mat_<double>(2, 3) << cos(angle_), -sin(angle_), 1, sin(angle_), cos(angle_), 1);
warpAffine(image, rotate_dst, rota_mat, image.size());
imshow("rotate_dst", rotate_dst);
}
三、仿射变换
Mat getAffineTransform( 返回变换矩阵
const Point2f src[], 变换前三个点的数组
const Point2f dst[] 变换后三个点的数组
);
void
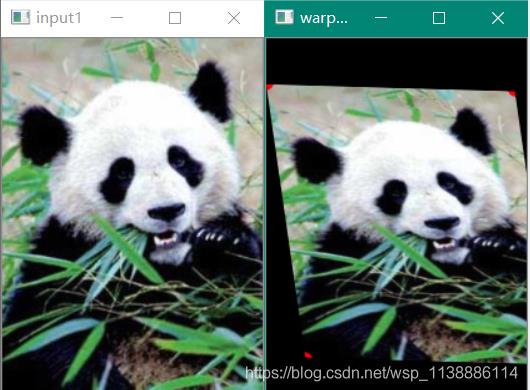
void QuickDemo::Affine_Demo(Mat& image) {
Mat warp_dst;
Mat warp_mat(2, 3, CV_32FC1);
Point2f srcTri[3];
Point2f dstTri[3];
/// 设置源图像和目标图像上的三组点以计算仿射变换
srcTri[0] = Point2f(0, 0);
srcTri[1] = Point2f(image.cols - 1, 0);
srcTri[2] = Point2f(0, image.rows - 1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 3; i++){
circle(image, srcTri[i], 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 5, 8);
}
dstTri[0] = Point2f(image.cols * 0.0, image.rows * 0.13);
dstTri[1] = Point2f(image.cols * 0.95, image.rows * 0.15);
dstTri[2] = Point2f(image.cols * 0.15, image.rows * 0.9);
warp_mat = getAffineTransform(srcTri, dstTri);
warpAffine(image, warp_dst, warp_mat, warp_dst.size());
imshow("warp_dst", warp_dst);
}
四、透视变换
获取透射变换的矩阵:
Mat getPerspectiveTransform( 返回变换矩阵
const Point2f src[], 透视变换前四个点的 数组
const Point2f dst[], 透视变换后四个点的 数组
int solveMethod = DECOMP_LU
)
透射变换
void warpPerspective( InputArray src, 原图像
OutputArray dst, 返回图像
InputArray M, 透视变换矩阵
Size dsize, 返回图像的大小(宽,高)
int flags = INTER_LINEAR, 插值方法
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, 边界处理
const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar() 缩放处理
)
void QuickDemo::toushi_Demo(Mat& image) {
Mat toushi_dst, toushi_mat;
Point2f toushi_before[4];
toushi_before[0] = Point2f(122, 220);
toushi_before[1] = Point2f(397, 121);
toushi_before[2] = Point2f(133, 339);
toushi_before[3] = Point2f(397, 218);
int width_0 = toushi_before[1].x - toushi_before[0].x;
int height_0 = toushi_before[1].y - toushi_before[0].y;
int width_1 = toushi_before[2].x - toushi_before[0].x;
int height_1 = toushi_before[2].y - toushi_before[0].y;
int width = (int)sqrt(width_0 * width_0 + height_0 * height_0);
int height = (int)sqrt(width_1 * width_1 + height_1 * height_1);
Point2f toushi_after[4];
toushi_after[0] = Point2f(2, 2); // x0, y0
toushi_after[1] = Point2f(width+2, 2); // x1, y0
toushi_after[2] = Point2f(2, height+2); // x0, y1
toushi_after[3] = Point2f(width + 2, height + 2); // x1, y1
for (size_t i = 0; i < 4; i++){
cout << toushi_after[i] << endl;
}
toushi_mat = getPerspectiveTransform(toushi_before, toushi_after);
warpPerspective(image, toushi_dst, toushi_mat, Size(width, height));
imshow("toushi_dst", toushi_dst);
}

综合示例
自动化透视矫正图像:
流程:
- 灰度化二值化
- 形态学去除噪点
- 获取轮廓
- 检测直线
- 计算直线交点
- 获取四个透视顶点
- 透视变换

inline void Intersection(Point2i& interPoint, Vec4i& line1, Vec4i& line2) {
// x1, y1, x2, y2 = line1[0], line1[1], line1[2], line1[3]
int A1 = line1[3] - line1[1];
int B1 = line1[0] - line1[2];
int C1 = line1[1] * line1[2] - line1[0] * line1[3];
int A2 = line2[3] - line2[1];
int B2 = line2[0] - line2[2];
int C2 = line2[1] * line2[2] - line2[0] * line2[3];
interPoint.x = static_cast<int>((B1 * C2 - B2 * C1) / (A1 * B2 - A2 * B1));
interPoint.y = static_cast<int>((C1 * A2 - A1 * C2) / (A1 * B2 - A2 * B1));
}
void QuickDemo::perspective_detect(Mat& image) {
Mat gray_dst, binary_dst, morph_dst;
// 二值化
cvtColor(image, gray_dst, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(gray_dst, binary_dst, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV | THRESH_OTSU);
//形态学操作
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(5, 5));
morphologyEx(binary_dst, morph_dst, MORPH_CLOSE, kernel, Point(-1, -1), 3);
bitwise_not(morph_dst, morph_dst);
imshow("morph_dst2", morph_dst);
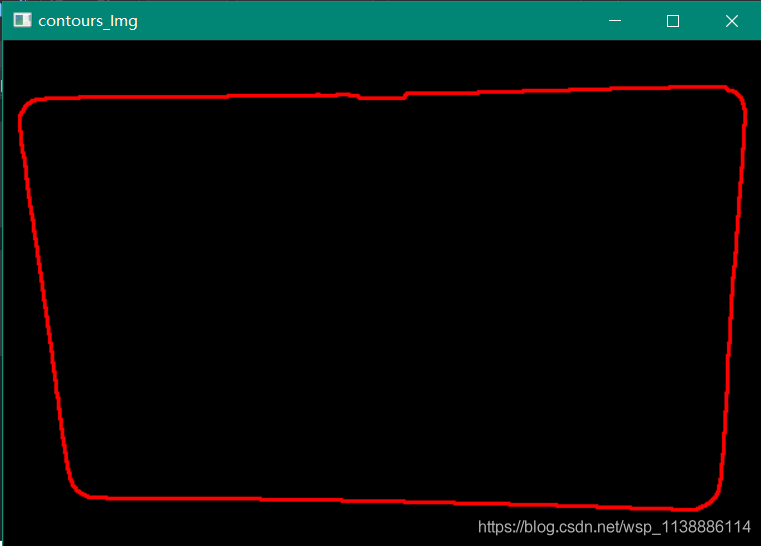
//轮廓查找与可视化
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarches;
int height = image.rows;
int width = image.cols;
Mat contours_Img = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_8UC3);
findContours(morph_dst, contours, hierarches, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
for (size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++){
Rect rect = boundingRect(contours[i]);
if (rect.width > width / 2 && rect.width < width - 5) {
drawContours(contours_Img, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, hierarches, 0, Point());
}
}
imshow("contours_Img", contours_Img);
vector<Vec4i> lines;
Mat houghImg;
int accu = min(width * 0.5, height * 0.5);
cvtColor(contours_Img, houghImg, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
HoughLinesP(houghImg, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, accu, accu*0.6, 0);
Mat lineImg = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_8UC3);
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++){
Vec4i ln = lines[i];
line(lineImg, Point(ln[0], ln[1]), Point(ln[2], ln[3]), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
}
// 寻找与定位上下左右四条直线
int delta = 0;
Vec4i topline = { 0, 0, 0, 0 };
Vec4i bottomline;
Vec4i leftline, rightline;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
Vec4i ln = lines[i];
delta = abs(ln[3] - ln[1]); // y2-y1
//topline
if (ln[3] < height / 2.0 && ln[1] < height / 2.0 && delta < accu - 1) {
if (topline[3] > ln[3] && topline[3] > 0) {
topline = lines[i];
}
else {
topline = lines[i];
}
}
if (ln[3] > height / 2.0 && ln[1] > height / 2.0 && delta < accu - 1) {
bottomline = lines[i];
}
if (ln[0] < width / 2.0 && ln[2] < width / 2.0) {
leftline = lines[i];
}
if (ln[0] > width / 2.0 && ln[2] > width / 2.0) {
rightline = lines[i];
}
}
cout << "topline: " << topline << endl;
cout << "bottomline: " << bottomline << endl;
cout << "leftline: " << leftline << endl;
cout << "rightline: " << rightline << endl;
// 计算上述四条直线交点(两条线的交点:依次为左上,右上,左下,右下)
Point2i p0, p1, p2, p3;
Intersection(p0, topline, leftline);
Intersection(p1, topline, rightline);
Intersection(p2, bottomline, leftline);
Intersection(p3, bottomline, rightline);
circle(lineImg, p0, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
circle(lineImg, p1, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
circle(lineImg, p2, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
circle(lineImg, p3, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
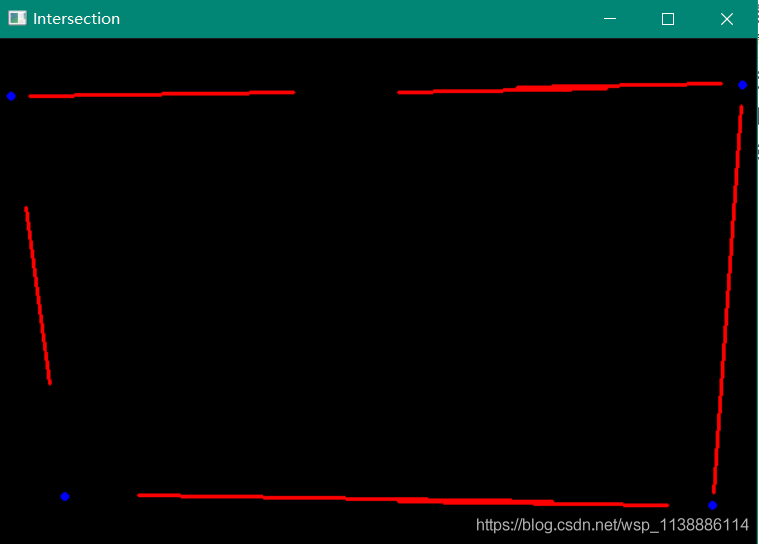
imshow("Intersection", lineImg);
//透视变换
vector<Point2f> src_point(4);
src_point[0] = p0;
src_point[1] = p1;
src_point[2] = p2;
src_point[3] = p3;
int new_height = max(abs(p2.y - p0.y), abs(p3.y - p1.y));
int new_width = max(abs(p1.x - p0.x), abs(p3.x - p2.x));
cout << "new_height = " << new_height << endl;
cout << "new_width = " << new_width << endl;
vector<Point2f> dst_point(4);
dst_point[0] = Point(0,0);
dst_point[1] = Point(new_width, 0);
dst_point[2] = Point(0, new_height);
dst_point[3] = Point(new_width, new_height);
Mat resultImg;
Mat wrap_mat = getPerspectiveTransform(src_point, dst_point);
warpPerspective(image, resultImg, wrap_mat, Size(new_width, new_height));
imshow("resultImg", resultImg);
}
关键步骤可视化

总结
到此这篇关于OpenCV和C++实现图像的翻转(镜像)、平移、旋转、仿射与透视变换的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关OpenCV和C++图像翻转平移旋转内容请搜索海外IDC网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持海外IDC网!
【文章出处:国内服务器】