python通过Seq2Seq实现闲聊机器人
目录
- 一、准备训练数据
- 二、数据的处理和保存
- 2.1 小黄鸡的语料的处理
- 2.2 微博语料的处理
- 2.3 处理后的结果
- 三、构造文本序列化和反序列化方法
- 四、构建Dataset和DataLoader
- 五、完成encoder编码器逻辑
- 六、完成decoder解码器的逻辑
- 七、完成seq2seq的模型
- 八、完成训练逻辑
- 九、评估逻辑
一、准备训练数据
主要的数据有两个:
1.小黄鸡的聊天语料:噪声很大

2.微博的标题和评论:质量相对较高

二、数据的处理和保存
由于数据中存到大量的噪声,可以对其进行基础的处理,然后分别把input和target使用两个文件保存,即input中的第N行尾问,target的第N行为答
后续可能会把单个字作为特征(存放在input_word.txt),也可能会把词语作为特征(input.txt)
2.1 小黄鸡的语料的处理
def format_xiaohuangji_corpus(word=False):
"""处理小黄鸡的语料"""
if word:
corpus_path = "./chatbot/corpus/xiaohuangji50w_nofenci.conv"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input_word.txt"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output_word.txt"
else:
corpus_path = "./chatbot/corpus/xiaohuangji50w_nofenci.conv"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input.txt"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output.txt"
f_input = open(input_path, "a")
f_output = open(output_path, "a")
pair = []
for line in tqdm(open(corpus_path), ascii=True):
if line.strip() == "E":
if not pair:
continue
else:
assert len(pair) == 2, "长度必须是2"
if len(pair[0].strip()) >= 1 and len(pair[1].strip()) >= 1:
f_input.write(pair[0] + "\n")
f_output.write(pair[1] + "\n")
pair = []
elif line.startswith("M"):
line = line[1:]
if word:
pair.append(" ".join(list(line.strip())))
else:
pair.append(" ".join(jieba_cut(line.strip())))
2.2 微博语料的处理
def format_weibo(word=False):
"""
微博数据存在一些噪声,未处理
:return:
"""
if word:
origin_input = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_post"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input_word.txt"
origin_output = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_response"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output_word.txt"
else:
origin_input = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_post"
input_path = "./chatbot/corpus/input.txt"
origin_output = "./chatbot/corpus/stc_weibo_train_response"
output_path = "./chatbot/corpus/output.txt"
f_input = open(input_path, "a")
f_output = open(output_path, "a")
with open(origin_input) as in_o, open(origin_output) as out_o:
for _in, _out in tqdm(zip(in_o, out_o), ascii=True):
_in = _in.strip()
_out = _out.strip()
if _in.endswith(")") or _in.endswith("」") or _in.endswith(")"):
_in = re.sub("(.*)|「.*?」|\(.*?\)", " ", _in)
_in = re.sub("我在.*?alink|alink|(.*?\d+x\d+.*?)|#|】|【|-+|_+|via.*?:*.*", " ", _in)
_in = re.sub("\s+", " ", _in)
if len(_in) < 1 or len(_out) < 1:
continue
if word:
_in = re.sub("\s+", "", _in) # 转化为一整行,不含空格
_out = re.sub("\s+", "", _out)
if len(_in) >= 1 and len(_out) >= 1:
f_input.write(" ".join(list(_in)) + "\n")
f_output.write(" ".join(list(_out)) + "\n")
else:
if len(_in) >= 1 and len(_out) >= 1:
f_input.write(_in.strip() + "\n")
f_output.write(_out.strip() + "\n")
f_input.close()
f_output.close()
2.3 处理后的结果

三、构造文本序列化和反序列化方法
和之前的操作相同,需要把文本能转化为数字,同时还需实现方法把数字转化为文本
示例代码:
import config
import pickle
class Word2Sequence():
UNK_TAG = "UNK"
PAD_TAG = "PAD"
SOS_TAG = "SOS"
EOS_TAG = "EOS"
UNK = 0
PAD = 1
SOS = 2
EOS = 3
def __init__(self):
self.dict = {
self.UNK_TAG: self.UNK,
self.PAD_TAG: self.PAD,
self.SOS_TAG: self.SOS,
self.EOS_TAG: self.EOS
}
self.count = {}
self.fited = False
def to_index(self, word):
"""word -> index"""
assert self.fited == True, "必须先进行fit操作"
return self.dict.get(word, self.UNK)
def to_word(self, index):
"""index -> word"""
assert self.fited, "必须先进行fit操作"
if index in self.inversed_dict:
return self.inversed_dict[index]
return self.UNK_TAG
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dict)
def fit(self, sentence):
"""
:param sentence:[word1,word2,word3]
:param min_count: 最小出现的次数
:param max_count: 最大出现的次数
:param max_feature: 总词语的最大数量
:return:
"""
for a in sentence:
if a not in self.count:
self.count[a] = 0
self.count[a] += 1
self.fited = True
def build_vocab(self, min_count=1, max_count=None, max_feature=None):
# 比最小的数量大和比最大的数量小的需要
if min_count is not None:
self.count = {k: v for k, v in self.count.items() if v >= min_count}
if max_count is not None:
self.count = {k: v for k, v in self.count.items() if v <= max_count}
# 限制最大的数量
if isinstance(max_feature, int):
count = sorted(list(self.count.items()), key=lambda x: x[1])
if max_feature is not None and len(count) > max_feature:
count = count[-int(max_feature):]
for w, _ in count:
self.dict[w] = len(self.dict)
else:
for w in sorted(self.count.keys()):
self.dict[w] = len(self.dict)
# 准备一个index->word的字典
self.inversed_dict = dict(zip(self.dict.values(), self.dict.keys()))
def transform(self, sentence, max_len=None, add_eos=False):
"""
实现吧句子转化为数组(向量)
:param sentence:
:param max_len:
:return:
"""
assert self.fited, "必须先进行fit操作"
r = [self.to_index(i) for i in sentence]
if max_len is not None:
if max_len > len(sentence):
if add_eos:
r += [self.EOS] + [self.PAD for _ in range(max_len - len(sentence) - 1)]
else:
r += [self.PAD for _ in range(max_len - len(sentence))]
else:
if add_eos:
r = r[:max_len - 1]
r += [self.EOS]
else:
r = r[:max_len]
else:
if add_eos:
r += [self.EOS]
# print(len(r),r)
return r
def inverse_transform(self, indices):
"""
实现从数组 转化为 向量
:param indices: [1,2,3....]
:return:[word1,word2.....]
"""
sentence = []
for i in indices:
word = self.to_word(i)
sentence.append(word)
return sentence
# 之后导入该word_sequence使用
word_sequence = pickle.load(open("./pkl/ws.pkl", "rb")) if not config.use_word else pickle.load(
open("./pkl/ws_word.pkl", "rb"))
if __name__ == '__main__':
from word_sequence import Word2Sequence
from tqdm import tqdm
import pickle
word_sequence = Word2Sequence()
# 词语级别
input_path = "../corpus/input.txt"
target_path = "../corpus/output.txt"
for line in tqdm(open(input_path).readlines()):
word_sequence.fit(line.strip().split())
for line in tqdm(open(target_path).readlines()):
word_sequence.fit(line.strip().split())
# 使用max_feature=5000个数据
word_sequence.build_vocab(min_count=5, max_count=None, max_feature=5000)
print(len(word_sequence))
pickle.dump(word_sequence, open("./pkl/ws.pkl", "wb"))
word_sequence.py:
class WordSequence(object):
PAD_TAG = 'PAD' # 填充标记
UNK_TAG = 'UNK' # 未知词标记
SOS_TAG = 'SOS' # start of sequence
EOS_TAG = 'EOS' # end of sequence
PAD = 0
UNK = 1
SOS = 2
EOS = 3
def __init__(self):
self.dict = {
self.PAD_TAG: self.PAD,
self.UNK_TAG: self.UNK,
self.SOS_TAG: self.SOS,
self.EOS_TAG: self.EOS
}
self.count = {} # 保存词频词典
self.fited = False
def to_index(self, word):
"""
word --> index
:param word:
:return:
"""
assert self.fited == True, "必须先进行fit操作"
return self.dict.get(word, self.UNK)
def to_word(self, index):
"""
index -- > word
:param index:
:return:
"""
assert self.fited, '必须先进行fit操作'
if index in self.inverse_dict:
return self.inverse_dict[index]
return self.UNK_TAG
def fit(self, sentence):
"""
传入句子,统计词频
:param sentence:
:return:
"""
for word in sentence:
# 对word出现的频率进行统计,当word不在sentence时,返回值是0,当word在sentence中时,返回+1,以此进行累计计数
# self.count[word] = self.dict.get(word, 0) + 1
if word not in self.count:
self.count[word] = 0
self.count[word] += 1
self.fited = True
def build_vocab(self, min_count=2, max_count=None, max_features=None):
"""
构造词典
:param min_count:最小词频
:param max_count: 最大词频
:param max_features: 词典中词的数量
:return:
"""
# self.count.pop(key),和del self.count[key] 无法在遍历self.count的同时进行删除key.因此浅拷贝temp后对temp遍历并删除self.count
temp = self.count.copy()
for key in temp:
cur_count = self.count.get(key, 0) # 当前词频
if min_count is not None:
if cur_count < min_count:
del self.count[key]
if max_count is not None:
if cur_count > max_count:
del self.count[key]
if max_features is not None:
self.count = dict(sorted(list(self.count.items()), key=lambda x: x[1], reversed=True)[:max_features])
for key in self.count:
self.dict[key] = len(self.dict)
# 准备一个index-->word的字典
self.inverse_dict = dict(zip(self.dict.values(), self.dict.keys()))
def transforms(self, sentence, max_len=10, add_eos=False):
"""
把sentence转化为序列
:param sentence: 传入的句子
:param max_len: 句子的最大长度
:param add_eos: 是否添加结束符
add_eos : True时,输出句子长度为max_len + 1
add_eos : False时,输出句子长度为max_len
:return:
"""
assert self.fited, '必须先进行fit操作!'
if len(sentence) > max_len:
sentence = sentence[:max_len]
# 提前计算句子长度,实现ass_eos后,句子长度统一
sentence_len = len(sentence)
# sentence[1,3,4,5,UNK,EOS,PAD,....]
if add_eos:
sentence += [self.EOS_TAG]
if sentence_len < max_len:
# 句子长度不够,用PAD来填充
sentence += (max_len - sentence_len) * [self.PAD_TAG]
# 对于新出现的词采用特殊标记
result = [self.dict.get(i, self.UNK) for i in sentence]
return result
def invert_transform(self, indices):
"""
序列转化为sentence
:param indices:
:return:
"""
# return [self.inverse_dict.get(i, self.UNK_TAG) for i in indices]
result = []
for i in indices:
if self.inverse_dict[i] == self.EOS_TAG:
break
result.append(self.inverse_dict.get(i, self.UNK_TAG))
return result
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dict)
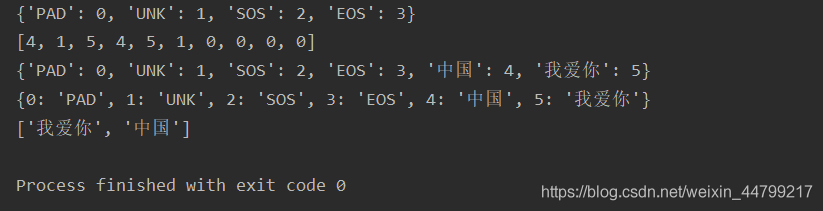
if __name__ == '__main__':
num_sequence = WordSequence()
print(num_sequence.dict)
str1 = ['中国', '您好', '我爱你', '中国', '我爱你', '北京']
num_sequence.fit(str1)
num_sequence.build_vocab()
print(num_sequence.transforms(str1))
print(num_sequence.dict)
print(num_sequence.inverse_dict)
print(num_sequence.invert_transform([5, 4])) # 这儿要传列表
运行结果:
四、构建Dataset和DataLoader
创建dataset.py 文件,准备数据集
import config
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from word_sequence import WordSequence
class ChatDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self):
self.input_path = config.chatbot_input_path
self.target_path = config.chatbot_target_path
self.input_lines = open(self.input_path, encoding='utf-8').readlines()
self.target_lines = open(self.target_path, encoding='utf-8').readlines()
assert len(self.input_lines) == len(self.target_lines), 'input和target长度不一致'
def __getitem__(self, item):
input = self.input_lines[item].strip().split()
target = self.target_lines[item].strip().split()
if len(input) == 0 or len(target) == 0:
input = self.input_lines[item + 1].strip().split()
target = self.target_lines[item + 1].strip().split()
# 此处句子的长度如果大于max_len,那么应该返回max_len
input_length = min(len(input), config.max_len)
target_length = min(len(target), config.max_len)
return input, target, input_length, target_length
def __len__(self):
return len(self.input_lines)
def collate_fn(batch):
# 1.排序
batch = sorted(batch, key=lambda x: x[2], reversed=True)
input, target, input_length, target_length = zip(*batch)
# 2.进行padding的操作
input = torch.LongTensor([WordSequence.transform(i, max_len=config.max_len) for i in input])
target = torch.LongTensor([WordSequence.transforms(i, max_len=config.max_len, add_eos=True) for i in target])
input_length = torch.LongTensor(input_length)
target_length = torch.LongTensor(target_length)
return input, target, input_length, target_length
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset=ChatDataset(), batch_size=config.batch_size, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn,
drop_last=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(len(data_loader))
for idx, (input, target, input_length, target_length) in enumerate(data_loader):
print(idx)
print(input)
print(target)
print(input_length)
print(target_length)
五、完成encoder编码器逻辑
encode.py:
import torch.nn as nn
import config
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_packed_sequence, pack_padded_sequence
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
# torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings词典大小即不重复词数,embedding_dim单个词用多长向量表示)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(
num_embeddings=len(config.word_sequence.dict),
embedding_dim=config.embedding_dim,
padding_idx=config.word_sequence.PAD
)
self.gru = nn.GRU(
input_size=config.embedding_dim,
num_layers=config.num_layer,
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
bidirectional=False,
batch_first=True
)
def forward(self, input, input_length):
"""
:param input: [batch_size, max_len]
:return:
"""
embedded = self.embedding(input) # embedded [batch_size, max_len, embedding_dim]
# 加速循环过程
embedded = pack_padded_sequence(embedded, input_length, batch_first=True) # 打包
out, hidden = self.gru(embedded)
out, out_length = pad_packed_sequence(out, batch_first=True, padding_value=config.num_sequence.PAD) # 解包
# hidden即h_n [num_layer*[1/2],batchsize, hidden_size]
# out : [batch_size, seq_len/max_len, hidden_size]
return out, hidden, out_length
if __name__ == '__main__':
from dataset import data_loader
encoder = Encoder()
print(encoder)
for input, target, input_length, target_length in data_loader:
out, hidden, out_length = encoder(input, input_length)
print(input.size())
print(out.size())
print(hidden.size())
print(out_length)
break
六、完成decoder解码器的逻辑
decode.py:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import config
import torch.nn.functional as F
from word_sequence import WordSequence
class Decode(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.max_seq_len = config.max_len
self.vocab_size = len(WordSequence)
self.embedding_dim = config.embedding_dim
self.dropout = config.dropout
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=self.vocab_size, embedding_dim=self.embedding_dim,
padding_idx=WordSequence.PAD)
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size=self.embedding_dim, hidden_size=config.hidden_size, num_layers=1, batch_first=True,
dropout=self.dropout)
self.log_softmax = nn.LogSoftmax()
self.fc = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.vocab_size)
def forward(self, encoder_hidden, target, target_length):
# encoder_hidden [batch_size,hidden_size]
# target [batch_size,seq-len]
decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[WordSequence.SOS]] * config.batch_size).to(config.device)
decoder_outputs = torch.zeros(config.batch_size, config.max_len, self.vocab_size).to(
config.device) # [batch_size,seq_len,14]
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # [batch_size,hidden_size]
for t in range(config.max_len):
decoder_output_t, decoder_hidden = self.forward_step(decoder_input, decoder_hidden)
decoder_outputs[:, t, :] = decoder_output_t
value, index = torch.topk(decoder_output_t, 1) # index [batch_size,1]
decoder_input = index
return decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden
def forward_step(self, decoder_input, decoder_hidden):
"""
:param decoder_input:[batch_size,1]
:param decoder_hidden:[1,batch_size,hidden_size]
:return:[batch_size,vocab_size],decoder_hidden:[1,batch_size,didden_size]
"""
embeded = self.embedding(decoder_input) # embeded: [batch_size,1 , embedding_dim]
out, decoder_hidden = self.gru(embeded, decoder_hidden) # out [1, batch_size, hidden_size]
out = out.squeeze(0)
out = F.log_softmax(self.fc(out), dim=1) # [batch_Size, vocab_size]
out = out.squeeze(0)
# print("out size:",out.size(),decoder_hidden.size())
return out, decoder_hidden
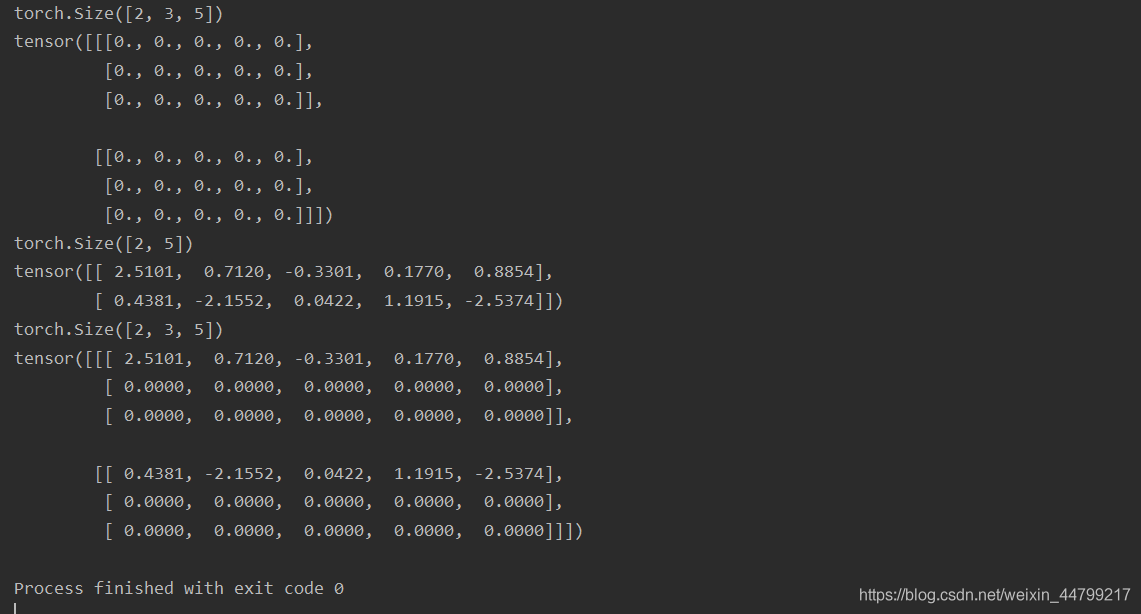
关于 decoder_outputs[:,t,:] = decoder_output_t的演示
decoder_outputs 形状 [batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size] decoder_output_t 形状[batch_size, vocab_size]
示例代码:
import torch a = torch.zeros((2, 3, 5)) print(a.size()) print(a) b = torch.randn((2, 5)) print(b.size()) print(b) a[:, 0, :] = b print(a.size()) print(a)
运行结果:
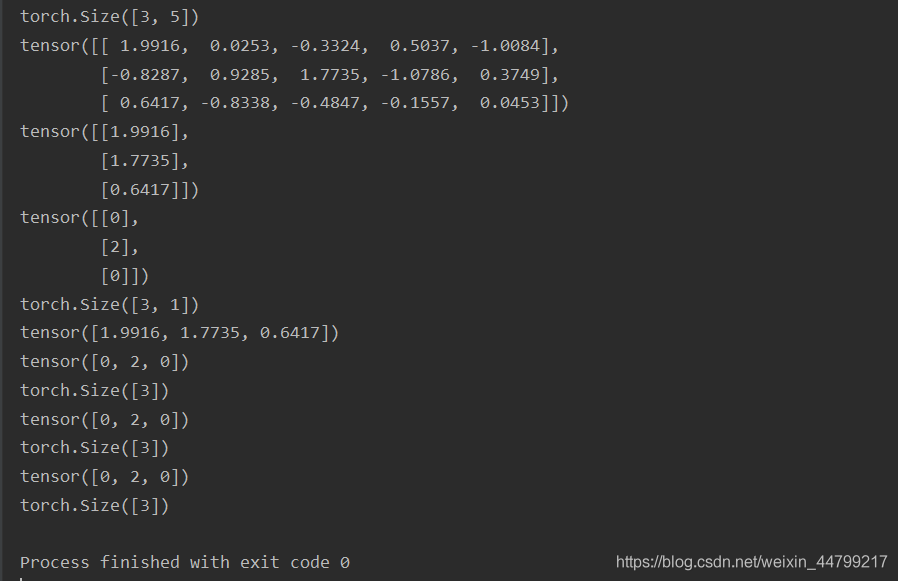
关于torch.topk, torch.max(),torch.argmax()
value, index = torch.topk(decoder_output_t , k = 1) decoder_output_t [batch_size, vocab_size]
示例代码:
import torch a = torch.randn((3, 5)) print(a.size()) print(a) values, index = torch.topk(a, k=1) print(values) print(index) print(index.size()) values, index = torch.max(a, dim=-1) print(values) print(index) print(index.size()) index = torch.argmax(a, dim=-1) print(index) print(index.size()) index = a.argmax(dim=-1) print(index) print(index.size())
运行结果:
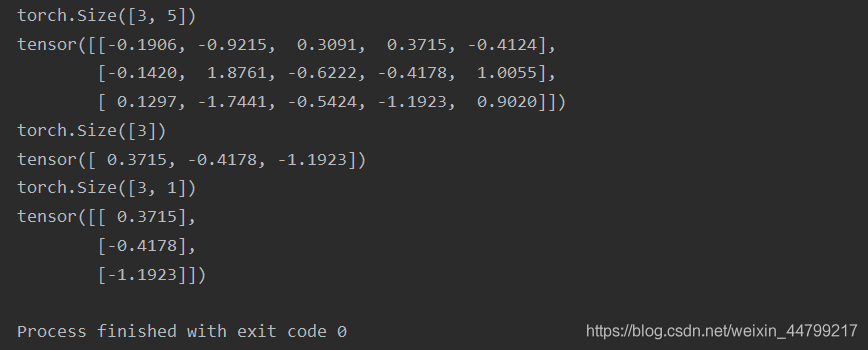
若使用teacher forcing ,将采用下次真实值作为下个time step的输入
# 注意unsqueeze 相当于浅拷贝,不会对原张量进行修改 decoder_input = target[:,t].unsqueeze(-1) target 形状 [batch_size, seq_len] decoder_input 要求形状[batch_size, 1]
示例代码:
import torch a = torch.randn((3, 5)) print(a.size()) print(a) b = a[:, 3] print(b.size()) print(b) c = b.unsqueeze(-1) print(c.size()) print(c)
运行结果:
七、完成seq2seq的模型
seq2seq.py:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder):
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, input, target, input_length, target_length):
encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = self.encoder(input, input_length)
decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden = self.decoder(encoder_hidden, target, target_length)
return decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden
def evaluation(self, inputs, input_length):
encoder_outputs, encoder_hidden = self.encoder(inputs, input_length)
decoded_sentence = self.decoder.evaluation(encoder_hidden)
return decoded_sentence
八、完成训练逻辑
为了加速训练,可以考虑在gpu上运行,那么在我们自顶一个所以的tensor和model都需要转化为CUDA支持的类型。
当前的数据量为500多万条,在GTX1070(8G显存)上训练,大概需要90分一个epoch,耐心的等待吧
train.py:
import torch
import config
from torch import optim
import torch.nn as nn
from encode import Encoder
from decode import Decoder
from seq2seq import Seq2Seq
from dataset import data_loader as train_dataloader
from word_sequence import WordSequence
encoder = Encoder()
decoder = Decoder()
model = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder)
# device在config文件中实现
model.to(config.device)
print(model)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model/seq2seq_model.pkl"))
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
optimizer.load_state_dict(torch.load("model/seq2seq_optimizer.pkl"))
criterion = nn.NLLLoss(ignore_index=WordSequence.PAD, reduction="mean")
def get_loss(decoder_outputs, target):
target = target.view(-1) # [batch_size*max_len]
decoder_outputs = decoder_outputs.view(config.batch_size * config.max_len, -1)
return criterion(decoder_outputs, target)
def train(epoch):
for idx, (input, target, input_length, target_len) in enumerate(train_dataloader):
input = input.to(config.device)
target = target.to(config.device)
input_length = input_length.to(config.device)
target_len = target_len.to(config.device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
##[seq_len,batch_size,vocab_size] [batch_size,seq_len]
decoder_outputs, decoder_hidden = model(input, target, input_length, target_len)
loss = get_loss(decoder_outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, idx * len(input), len(train_dataloader.dataset),
100. * idx / len(train_dataloader), loss.item()))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "model/seq2seq_model.pkl")
torch.save(optimizer.state_dict(), 'model/seq2seq_optimizer.pkl')
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(10):
train(i)
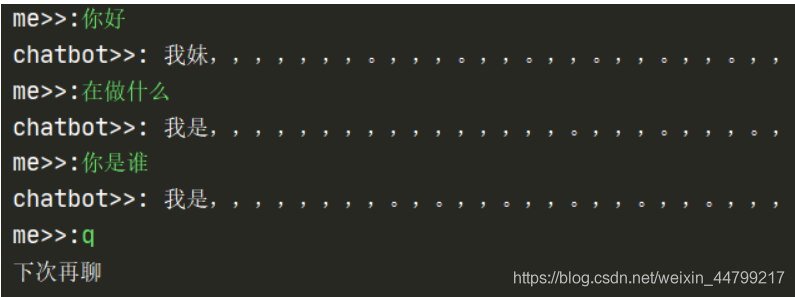
训练10个epoch之后的效果如下,可以看出损失依然很高:
Train Epoch: 9 [2444544/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.923604 Train Epoch: 9 [2444800/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.364594 Train Epoch: 9 [2445056/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.613254 Train Epoch: 9 [2445312/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.143538 Train Epoch: 9 [2445568/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.412729 Train Epoch: 9 [2445824/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.516526 Train Epoch: 9 [2446080/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.124945 Train Epoch: 9 [2446336/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.777015 Train Epoch: 9 [2446592/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.358538 Train Epoch: 9 [2446848/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.513412 Train Epoch: 9 [2447104/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.202757 Train Epoch: 9 [2447360/4889919 (50%)] Loss: 4.589584
九、评估逻辑
decoder 中添加评估方法
def evaluate(self, encoder_hidden): """ 评估, 和fowward逻辑类似 :param encoder_hidden: encoder最后time step的隐藏状态 [1, batch_size, hidden_size] :return: """ batch_size = encoder_hidden.size(1) # 初始化一个[batch_size, 1]的SOS张量,作为第一个time step的输出 decoder_input = torch.LongTensor([[config.target_ws.SOS]] * batch_size).to(config.device) # encoder_hidden 作为decoder第一个时间步的hidden [1, batch_size, hidden_size] decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # 初始化[batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size]的outputs 拼接每个time step结果 decoder_outputs = torch.zeros((batch_size, config.chatbot_target_max_len, self.vocab_size)).to(config.device) # 初始化一个空列表,存储每次的预测序列 predict_result = [] # 对每个时间步进行更新 for t in range(config.chatbot_target_max_len): decoder_output_t, decoder_hidden = self.forward_step(decoder_input, decoder_hidden) # 拼接每个time step,decoder_output_t [batch_size, vocab_size] decoder_outputs[:, t, :] = decoder_output_t # 由于是评估,需要每次都获取预测值 index = torch.argmax(decoder_output_t, dim = -1) # 更新下一时间步的输入 decoder_input = index.unsqueeze(1) # 存储每个时间步的预测序列 predict_result.append(index.cpu().detach().numpy()) # [[batch], [batch]...] ->[seq_len, vocab_size] # 结果转换为ndarry,每行是一个预测结果即单个字对应的索引, 所有行为seq_len长度 predict_result = np.array(predict_result).transpose() # (batch_size, seq_len)的array return decoder_outputs, predict_result
eval.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from dataset import get_dataloader
import config
import numpy as np
from Seq2Seq import Seq2SeqModel
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
model = Seq2SeqModel().to(config.device)
if os.path.exists('./model/chatbot_model.pkl'):
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/chatbot_model.pkl'))
def eval():
model.eval()
loss_list = []
test_data_loader = get_dataloader(train = False)
with torch.no_grad():
bar = tqdm(test_data_loader, desc = 'testing', total = len(test_data_loader))
for idx, (input, target, input_length, target_length) in enumerate(bar):
input = input.to(config.device)
target = target.to(config.device)
input_length = input_length.to(config.device)
target_length = target_length.to(config.device)
# 获取模型的预测结果
decoder_outputs, predict_result = model.evaluation(input, input_length)
# 计算损失
loss = F.nll_loss(decoder_outputs.view(-1, len(config.target_ws)), target.view(-1), ignore_index = config.target_ws.PAD)
loss_list.append(loss.item())
bar.set_description('idx{}:/{}, loss:{}'.format(idx, len(test_data_loader), np.mean(loss_list)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
eval()
interface.py:
from cut_sentence import cut
import torch
import config
from Seq2Seq import Seq2SeqModel
import os
# 模拟聊天场景,对用户输入进来的话进行回答
def interface():
# 加载训练集好的模型
model = Seq2SeqModel().to(config.device)
assert os.path.exists('./model/chatbot_model.pkl') , '请先对模型进行训练!'
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/chatbot_model.pkl'))
model.eval()
while True:
# 输入进来的原始字符串,进行分词处理
input_string = input('me>>:')
if input_string == 'q':
print('下次再聊')
break
input_cuted = cut(input_string, by_word = True)
# 进行序列转换和tensor封装
input_tensor = torch.LongTensor([config.input_ws.transfrom(input_cuted, max_len = config.chatbot_input_max_len)]).to(config.device)
input_length_tensor = torch.LongTensor([len(input_cuted)]).to(config.device)
# 获取预测结果
outputs, predict = model.evaluation(input_tensor, input_length_tensor)
# 进行序列转换文本
result = config.target_ws.inverse_transform(predict[0])
print('chatbot>>:', result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
interface()
config.py:
import torch
from word_sequence import WordSequence
chatbot_input_path = './corpus/input.txt'
chatbot_target_path = './corpus/target.txt'
word_sequence = WordSequence()
max_len = 9
batch_size = 128
embedding_dim = 100
num_layer = 1
hidden_size = 64
dropout = 0.1
model_save_path = './model.pkl'
optimizer_save_path = './optimizer.pkl'
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
cut.py:
"""
分词
"""
import jieba
import config1
import string
import jieba.posseg as psg # 返回词性
from lib.stopwords import stopwords
# 加载词典
jieba.load_userdict(config1.user_dict_path)
# 准备英文字符
letters = string.ascii_lowercase + '+'
def cut_sentence_by_word(sentence):
"""实现中英文分词"""
temp = ''
result = []
for word in sentence:
if word.lower() in letters:
# 如果是英文字符,则进行拼接空字符串
temp += word
else:
# 遇到汉字后,把英文先添加到结果中
if temp != '':
result.append(temp.lower())
temp = ''
result.append(word.strip())
if temp != '':
# 若英文出现在最后
result.append(temp.lower())
return result
def cut(sentence, by_word=False, use_stopwords=True, with_sg=False):
"""
:param sentence: 句子
:param by_word: T根据单个字分词或者F句子
:param use_stopwords: 是否使用停用词,默认False
:param with_sg: 是否返回词性
:return:
"""
if by_word:
result = cut_sentence_by_word(sentence)
else:
result = psg.lcut(sentence)
# psg 源码返回i.word,i.flag 即词,定义的词性
result = [(i.word, i.flag) for i in result]
# 是否返回词性
if not with_sg:
result = [i[0] for i in result]
# 是否使用停用词
if use_stopwords:
result = [i for i in result if i not in stopwords]
return result
到此这篇关于python通过Seq2Seq实现闲聊机器人的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Seq2Seq实现闲聊机器人内容请搜索hwidc以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持hwidc!
