OpenCV物体跟踪树莓派视觉小车实现过程学习
目录
- 物体跟踪效果展示
- 一、初始化
- 二、运动控制函数
- 三、舵机角度控制
- 四、摄像头&&图像处理
- 1、打开摄像头
- 2、把图像转换为灰度图
- 3、 高斯滤波(去噪)
- 4、亮度增强
- 5、转换为二进制
- 6、闭运算处理
- 7、获取轮廓
- 代码
- 五、获取最大轮廓坐标
- 六、运动
- 1、没有识别到轮廓(静止)
- 2、向前走
- 3、向左转
- 4、向右转
- 代码
- 总代码
物体跟踪效果展示





过程:
一、初始化
def Motor_Init():
global L_Motor, R_Motor
L_Motor= GPIO.PWM(l_motor,100)
R_Motor = GPIO.PWM(r_motor,100)
L_Motor.start(0)
R_Motor.start(0)
def Direction_Init():
GPIO.setup(left_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(left_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(l_motor,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(r_motor,GPIO.OUT)
def Servo_Init():
global pwm_servo
pwm_servo=Adafruit_PCA9685.PCA9685()
def Init():
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
Direction_Init()
Servo_Init()
Motor_Init()
二、运动控制函数
def Front(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Back(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Left(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Right(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Stop():
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
三、舵机角度控制
def set_servo_angle(channel,angle):
angle=4096*((angle*11)+500)/20000
pwm_servo.set_pwm_freq(50) #frequency==50Hz (servo)
pwm_servo.set_pwm(channel,0,int(angle))
set_servo_angle(4, 110) #top servo lengthwise
#0:back 180:front
set_servo_angle(5, 90) #bottom servo crosswise
#0:left 180:right
上面的(4):是顶部的舵机(摄像头上下摆动的那个舵机)
下面的(5):是底部的舵机(摄像头左右摆动的那个舵机)
四、摄像头&&图像处理
# 1 Image Process
img, contours = Image_Processing()
width, height = 160, 120
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
camera.set(3,width)
camera.set(4,height)
1、打开摄像头
打开摄像头,并设置窗口大小。
设置小窗口的原因: 小窗口实时性比较好。
# Capture the frames
ret, frame = camera.read()
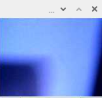
2、把图像转换为灰度图
# to gray
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('gray',gray)

3、 高斯滤波(去噪)
# Gausi blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
4、亮度增强
#brighten
blur = cv2.convertScaleAbs(blur, None, 1.5, 30)
5、转换为二进制
#to binary
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(blur,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
cv2.imshow('binary',binary)
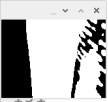
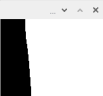
6、闭运算处理
#Close
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (17,17))
close = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow('close',close)
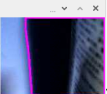
7、获取轮廓
#get contours
binary_c,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(close, 1, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cv2.drawContours(image, contours, -1, (255,0,255), 2)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
代码
def Image_Processing():
# Capture the frames
ret, frame = camera.read()
# Crop the image
image = frame
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# to gray
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('gray',gray)
# Gausi blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
#brighten
blur = cv2.convertScaleAbs(blur, None, 1.5, 30)
#to binary
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(blur,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
cv2.imshow('binary',binary)
#Close
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (17,17))
close = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow('close',close)
#get contours
binary_c,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(close, 1, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cv2.drawContours(image, contours, -1, (255,0,255), 2)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
return frame, contours
五、获取最大轮廓坐标
由于有可能出现多个物体,我们这里只识别最大的物体(深度学习可以搞分类,还没学到这,学到了再做),得到它的坐标。
# 2 get coordinates
x, y = Get_Coord(img, contours)
def Get_Coord(img, contours):
image = img.copy()
try:
contour = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea)
cv2.drawContours(image, contour, -1, (255,0,255), 2)
cv2.imshow('new_frame', image)
# get coord
M = cv2.moments(contour)
x = int(M['m10']/M['m00'])
y = int(M['m01']/M['m00'])
print(x, y)
return x,y
except:
print 'no objects'
return 0,0
返回最大轮廓的坐标:

六、运动
根据反馈回来的坐标,判断它的位置,进行运动。
# 3 Move
Move(x,y)
1、没有识别到轮廓(静止)
if x==0 and y==0:
Stop()
2、向前走
识别到物体,且在正中央(中间1/2区域),让物体向前走。
#go ahead
elif width/4 <x and x<(width-width/4):
Front(70)
3、向左转
物体在左边1/4区域。
#left
elif x < width/4:
Left(50)
4、向右转
物体在右边1/4区域。
#Right
elif x > (width-width/4):
Right(50)
代码
def Move(x,y):
global second
#stop
if x==0 and y==0:
Stop()
#go ahead
elif width/4 <x and x<(width-width/4):
Front(70)
#left
elif x < width/4:
Left(50)
#Right
elif x > (width-width/4):
Right(50)
总代码
#Object Tracking
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import Adafruit_PCA9685
import numpy as np
import cv2
second = 0
width, height = 160, 120
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
camera.set(3,width)
camera.set(4,height)
l_motor = 18
left_front = 22
left_back = 27
r_motor = 23
right_front = 25
right_back = 24
def Motor_Init():
global L_Motor, R_Motor
L_Motor= GPIO.PWM(l_motor,100)
R_Motor = GPIO.PWM(r_motor,100)
L_Motor.start(0)
R_Motor.start(0)
def Direction_Init():
GPIO.setup(left_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(left_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(l_motor,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_front,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(right_back,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(r_motor,GPIO.OUT)
def Servo_Init():
global pwm_servo
pwm_servo=Adafruit_PCA9685.PCA9685()
def Init():
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
Direction_Init()
Servo_Init()
Motor_Init()
def Front(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Back(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Left(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,1) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,1) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def Right(speed):
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(left_front,1) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(speed)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,1) #right_back
def Stop():
L_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(left_front,0) #left_front
GPIO.output(left_back,0) #left_back
R_Motor.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
GPIO.output(right_front,0) #right_front
GPIO.output(right_back,0) #right_back
def set_servo_angle(channel,angle):
angle=4096*((angle*11)+500)/20000
pwm_servo.set_pwm_freq(50) #frequency==50Hz (servo)
pwm_servo.set_pwm(channel,0,int(angle))
def Image_Processing():
# Capture the frames
ret, frame = camera.read()
# Crop the image
image = frame
cv2.imshow('frame',frame)
# to gray
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('gray',gray)
# Gausi blur
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0)
#brighten
blur = cv2.convertScaleAbs(blur, None, 1.5, 30)
#to binary
ret,binary = cv2.threshold(blur,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
cv2.imshow('binary',binary)
#Close
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (17,17))
close = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow('close',close)
#get contours
binary_c,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(close, 1, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
cv2.drawContours(image, contours, -1, (255,0,255), 2)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
return frame, contours
def Get_Coord(img, contours):
image = img.copy()
try:
contour = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea)
cv2.drawContours(image, contour, -1, (255,0,255), 2)
cv2.imshow('new_frame', image)
# get coord
M = cv2.moments(contour)
x = int(M['m10']/M['m00'])
y = int(M['m01']/M['m00'])
print(x, y)
return x,y
except:
print 'no objects'
return 0,0
def Move(x,y):
global second
#stop
if x==0 and y==0:
Stop()
#go ahead
elif width/4 <x and x<(width-width/4):
Front(70)
#left
elif x < width/4:
Left(50)
#Right
elif x > (width-width/4):
Right(50)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Init()
set_servo_angle(4, 110) #top servo lengthwise
#0:back 180:front
set_servo_angle(5, 90) #bottom servo crosswise
#0:left 180:right
while 1:
# 1 Image Process
img, contours = Image_Processing()
# 2 get coordinates
x, y = Get_Coord(img, contours)
# 3 Move
Move(x,y)
# must include this codes(otherwise you can't open camera successfully)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
Stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
break
#Front(50)
#Back(50)
#$Left(50)
#Right(50)
#time.sleep(1)
#Stop()
检测原理是基于最大轮廓的检测,没有用深度学习的分类,所以容易受到干扰,后期学完深度学习会继续优化。有意见或者想法的朋友欢迎交流。
以上就是OpenCV物体跟踪树莓派视觉小车实现过程学习的详细内容,更多关于OpenCV物体跟踪树莓派视觉小车的资料请关注hwidc其它相关文章!
【本文由:防cc 提供,感恩】