SpringBoot2.1.4中的错误处理机制
目录
- SpringBoot 2.1.4 错误处理机制
- SpringBoot错误机制原理
- SpringBoot 2.1.3 错误处理机制
- 引用的问题做个标记
- 错误处理机制
SpringBoot 2.1.4 错误处理机制
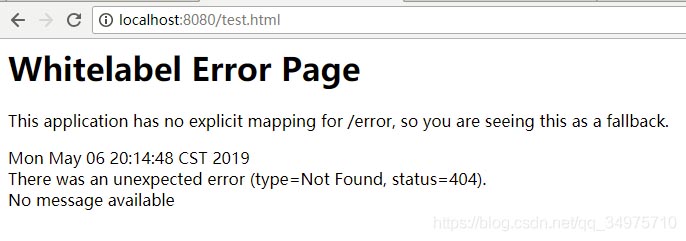
springboot的自动配置中帮我们配置了相关的错误处理组件,例如访问一个不存在的页面,就会出现下面的错误页面,上面也会显示相应的信息
在Postman软件中模拟移动端访问,会获取如下响应的json数据:
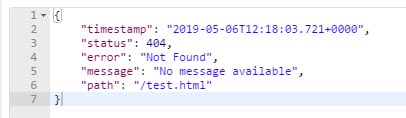
可以发现springboot的错误处理机制很好的适应了不同客户端访问,浏览器返回页面,移动端返回json,那这背后springboot是如何处理的,显示的页面我想自己设计,或者返回的这些信息我们自己能够定制吗?
SpringBoot错误机制原理
springboot版本:2.1.4.RELEASE
1、默认错误页面生成机制
当我们在访问一个不存在的路径时,会出现上面的错误页面,这个页面不是我们自己创建的,而是由springboot帮我们生成的,那下面我们首先弄清楚这个默认的错误页面(Whitelabel Error Page)是怎么生成的。
1.1 springboot关于error的自动配置
在package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error包下有如下的类:
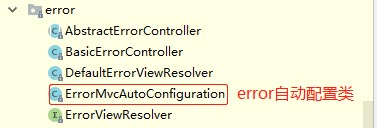
- BasicErrorController、AbstractErrorController:错误请求控制器
- DefaultErrorViewResolver:错误视图解析器
- ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration:error的自动配置类
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
在这个配置类中注册了一些组件:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorAttributes.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
// 关于error错误信息的相关类
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorController.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
// 处理错误请求的控制器
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(), this.errorViewResolvers);
}
@Bean
// 错误页面定制器
public ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer() {
return new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, this.dispatcherServletPath);
}
第一步:ErrorPageCustomizer
private static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties properties;
private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath;
protected ErrorPageCustomizer(ServerProperties properties, DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
this.properties = properties;
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
}
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
// getPath()获取到一个路径“/error”
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
// 关键点:这里讲将/error的errorPage注册到了servlet,在发生异常时就会转发到/error
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(new ErrorPage[]{errorPage});
}
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
注意上面的注释,这里是为什么发生错误就会发起/error,很多博客都未说明,当然这里没有讨论其内部原理。
第二步:BasicErrorController
在错误发生后,发起 “/error” 请求,那这个 “/error” 就会由上面已经注册的BasicErrorController 接收处理。
@Controller // 表明是个控制器
@RequestMapping({"${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}"}) // 映射的路径:/error
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
public BasicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties) {
this(errorAttributes, errorProperties, Collections.emptyList());
}
public BasicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties, List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
super(errorAttributes, errorViewResolvers);
Assert.notNull(errorProperties, "ErrorProperties must not be null");
this.errorProperties = errorProperties;
}
public String getErrorPath() {
return this.errorProperties.getPath();
}
// 处理浏览器的请求
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
// 处理移动端的请求
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
protected boolean isIncludeStackTrace(HttpServletRequest request, MediaType produces) {
IncludeStacktrace include = this.getErrorProperties().getIncludeStacktrace();
if (include == IncludeStacktrace.ALWAYS) {
return true;
} else {
return include == IncludeStacktrace.ON_TRACE_PARAM ? this.getTraceParameter(request) : false;
}
}
protected ErrorProperties getErrorProperties() {
return this.errorProperties;
}
}
这里可以解决一个疑惑,springboot怎么区分是浏览器还是移动端的,主要看这个方法的注解 produces={“text/html”} ,表示响应的数据是以html形式返回,这样当浏览器访问时就会调用这个方法
@RequestMapping(produces = {"text/html"})
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
...
客户端访问时就会调用下面的error方法。
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
下面再来具体分析默认错误页面如何生成,还是来看到errorHTML方法:
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
// 获取错误状态码,封装到HttpStatus里面
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
// 获取错误信息,以map形式返回,这个后面我们具体来看,到底我们能获取到哪些数据
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
// 设置响应体中状态码
response.setStatus(status.value());
// 关键点:这里就是在创建视图对象
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
下面来看这个resolveErrorView方法,这个方法是父类AbstractErrorController 中的:
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
// errorViewResolvers是一个list,存放ErrorViewResolver对象
Iterator var5 = this.errorViewResolvers.iterator();
ModelAndView modelAndView;
// 遍历集合
do {
if (!var5.hasNext()) {
return null;
}
ErrorViewResolver resolver = (ErrorViewResolver)var5.next();
// 关键点:解析器对象进行视图解析
modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
} while(modelAndView == null);
return modelAndView;
}
这里的resolveErrorView方法属于DefaultErrorViewResolver:
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 调用下面的方法解析视图,传入参数为错误状态码,错误信息的map
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = this.resolve((String)SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 定义视图名,这里我们可以确定视图名:error/错误码,例如:error/404,
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
// 这里结合上面的errorViewName,其实就是在template目录下的error目录进行查找
// 我们默认情况下是没有error目录,这里的provide最终值为null,代码较多就不一一展示,有兴趣的可以跟下去
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
// 根据判定,这里会接着调用下面的resolveResource方法
return provider != null ? new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model) : this.resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// getStaticLocations()获取的是静态资源路径:"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/","classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"
String[] var3 = this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations();
int var4 = var3.length;
// 遍历上面的4个静态资源路径
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String location = var3[var5];
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
// 创建resource对象,例如error/404.html
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
// 查找在对应静态资源目录下是否有上面的这个资源对象,有就创建视图对象
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new DefaultErrorViewResolver.HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
} catch (Exception var8) {
;
}
}
// 都没找到就返回null,默认情况下是不存在error目录的,所以这里最终返回null
return null;
}
当resolveResource方法执行完返回null,resolve方法也就返回null,在回到resolveErrorView
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 调用下面的方法解析视图,传入参数为错误状态码,错误信息的map
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
// 上面分析得到modelAndView的值为null,下面的if中SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())是在判断错误码的首位是否为1,2,3,4,5,这个大家下去可以跟一下
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = this.resolve((String)SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
// if里面的resolve方法分析跟上面一样,默认情况下是没有4xx.html/5xx.html页面文件的,所以最终这里返回null
return modelAndView;
}
这个resolveErrorView方法执行完后,我们就可以回到最开始处理 “/error” 请求的errorHtml方法了
@RequestMapping(produces = {"text/html"} )
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
// modelAnView根据上面的分析其值为null
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
当modelAndView为null时,将会执行'new ModelAndView(“error”, model),那这个“error”又是什么呢?看下面WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration 里面有个组件其 name就是error,这个组件是StaticView,就是一个View,里面的视图渲染方法render中的内容就是最开始我们看到的那个错误页面的内容。
@Conditional({ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorTemplateMissingCondition.class})
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView defaultErrorView = new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView();
protected WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration() {
}
@Bean(name = {"error"})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = {"error"})
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}
...
}
private static class StaticView implements View {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView.class);
private StaticView() {
}
public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
String message = this.getMessage(model);
logger.error(message);
} else {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
Date timestamp = (Date)model.get("timestamp");
Object message = model.get("message");
Object trace = model.get("trace");
if (response.getContentType() == null) {
response.setContentType(this.getContentType());
}
builder.append("<html><body><h1>Whitelabel Error Page</h1>").append("<p>This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.</p>").append("<div id='created'>").append(timestamp).append("</div>").append("<div>There was an unexpected error (type=").append(this.htmlEscape(model.get("error"))).append(", status=").append(this.htmlEscape(model.get("status"))).append(").</div>");
if (message != null) {
builder.append("<div>").append(this.htmlEscape(message)).append("</div>");
}
if (trace != null) {
builder.append("<div style='white-space:pre-wrap;'>").append(this.htmlEscape(trace)).append("</div>");
}
builder.append("</body></html>");
response.getWriter().append(builder.toString());
}
}
private String htmlEscape(Object input) {
return input != null ? HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(input.toString()) : null;
}
private String getMessage(Map<String, ?> model) {
Object path = model.get("path");
String message = "Cannot render error page for request [" + path + "]";
if (model.get("message") != null) {
message = message + " and exception [" + model.get("message") + "]";
}
message = message + " as the response has already been committed.";
message = message + " As a result, the response may have the wrong status code.";
return message;
}
public String getContentType() {
return "text/html";
}
}
所以,整个大致的过程到此结束了,默认情况下错误请求处理完成后就返回的这个StaticView定义的页面,下图做个基本的梳理。后续再来做自定义错误页面、自定义错误数据的原理分析。

SpringBoot 2.1.3 错误处理机制
引用的问题做个标记
以前的引用好像在新版本中无法引用了
错误处理机制
其他的程序的类的声明直接用IDEA的提示来用就可以了。
如果还是有错误的话,就进入到lib中看看引用的类的方法就可以了
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigration.web.DefaultErrorAttributes;//这是以前的 import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes;//这是现在的
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
【文章出处:cc防御 转载请说明出处】