java基础javeSE程序逻辑控制语法
目录
- 顺序结构
- 分支结构
- if 语句
- 悬垂 else
- switch 语句
- 循环结构
- while 循环
- for 循环
- do while 循环
- 输入输出方式
- 输出到控制台
- 从键盘输入
- 猜数字游戏
顺序结构
按照代码书写的顺序一行一行执行
分支结构
if 语句
基本语法形式:
if(布尔表达式){
//条件满足时执行代码
}
if(布尔表达式){
//条件满足时执行代码
}else{
//条件不满足时执行代码
}
//多分支
if(布尔表达式){
//条件满足时执行代码
}else if(布尔表达式){
//条件满足时执行代码
}else{
//条件都不满足时执行代码
}
注意:条件表达式必须是布尔值
示例:
int a = 10;
if(a){
System.out.println(a);
}//err
//对于while等循环语句也一样
悬垂 else
示例:
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
if (x == 10)
if (y == 10)
System.out.println("aaa");
else
System.out.println("bbb");
注:if / else语句中可以不加大括号,但只能写一条语句;此时else和最接近的 if 匹配
switch 语句
基本语法:
switch(整数|枚举|字符|字符串){
case 内容1 : {
内容满足时执行语句;
[break;]
}
case 内容2 : {
内容满足时执行语句;
[break;]
}
...
default:{
内容都不满足时执行语句;
[break;]
}
}
switch(表达式) 中表达式接收的类型包括:
整数(只包括byte、short、int)
字符(char)
字符串(String)
枚举类型(区别C语言)
循环结构
基本上与C语言语法一致
注意:
while 循环
while (表达式) 中的表达式必须是布尔值
break :让最靠近包裹它的整个循环提前结束
continue :跳过本次循环,立即进入下次循环
for 循环
for(表达式1;表达式2;表达式3) 中的表达式2是循环的判断条件,要使用布尔值
do while 循环
while 中的循环条件只能是布尔值
输入输出方式
输出到控制台
基本语法:
System.out.println(msg); // 输出一个字符串,自带换行 System.out.print(msg); // 输出一个字符串,不带换行 System.out.printf(format,msg); // 格式化输出,括号内内容类似于 C 语言的 printf
格式化输出表:
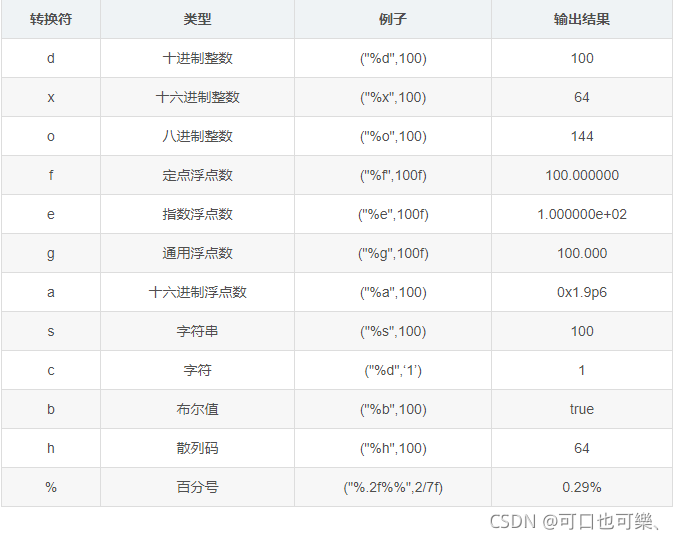
从键盘输入
读取字符/字符串/整数/浮点数/布尔值
首先需要导入 util 包 import java.util.Scanner;然后再构造一个 Scanner 对象并与”标准输入流“ System.in 关联:
Scanner 对象名 = new Scanner(System.in);
示例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = in.nextInt(); //读入一个整数
double b = in.nextDouble(); //读入一个浮点数
boolean c = in.nextBoolean(); //读入一个布尔值
String s = in.next(); //读入一个字符串
//上述读入字符串是按空白符当作分隔符的,故只能读入第一个空格之前的字符
//如果想要读取该行的所有字符(包含空格)则:
String s = in.nextLine();
//如果这行代码上面还有其他读入的语句,可能这行代码就不会执行
//因为上一行的回车可能被它读入,直接这行结束
//解决方案:将其放在读入代码的第一个或者在它前面加一个 in.nextLine(); 来读取掉之前的回车
}
}
输入多组数据
示例:
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNextInt()){
int a = in.nextInt();
// 内容
}
结束:输入 Ctrl + D 或者Ctrl + Z 结束
猜数字游戏
随机数生成:
需要导入 util 包 import java.util.Random;
示例:
import java.util.Random;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new random(); // 默认随机种子是系统时间
int rand = random.nextInt(bound:100) + 1;
// random.nextInt(bound:100) 是生成[0,100)间的随机整数
}
}
最终代码:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Random random = new Random();
int rand = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
while (true){
System.out.print("请输入你所猜测的数字:");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
if(num == rand){
System.out.println("恭喜你,猜对了!");
break;
}else if(num < rand){
System.out.println("很遗憾,你猜的数字小了!");
}else{
System.out.println("很遗憾,你猜的数字大了!");
}
}
}
}
以上就是java基础javeSE程序逻辑控制语法的详细内容,更多关于javeSE程序逻辑控制的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
【转自:http://www.1234xp.com/kt.html 转载请说明出处】