OpenCV结合selenium实现滑块验证码
本次案例使用OpenCV和selenium来解决一下滑块验证码
先说一下思路:
- 弹出滑块验证码后使用selenium元素截图将验证码整个背景图截取出来
- 将需要滑动的小图单独截取出来,最好将小图与背景图顶部的像素距离获取到,这样可以将背景图上下多余的边框截取掉
- 使用OpenCV将背景图和小图进行灰度处理,并对小图再次进行二值化全局阈值,这样就可以利用OpenCV在背景图中找到小图所在的位置
- 用OpenCV获取到相差的距离后利用selenium的鼠标拖动方法进行拖拉至终点。
详细步骤:
先获取验证码背景图,selenium浏览器对象中使用screenshot方法可以将指定的元素图片截取出来
import os
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get("https://www.toutiao.com/c/user/token/MS4wLjABAAAA4EKNlqVeNTTuEdWn0VytNS8cdODKTsNNwLTxOnigzZtclro2Kylvway5mTyTUKvz/")
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), "Desktop", "background.png")
browser.find_element_by_id("element_id_name").screenshot(save_path)
截取后的验证码背景图和需要滑动的小图 如:

再将小图与背景图顶部的像素距离获取到,指的是下面图中红边的高度:

如果HTML元素中小图是单独存在时,那么它的高度在会定义在页面元素中,使用selenium页面元素对象的value_of_css_property方法可以获取到像素距离。
获取这个是因为要把背景图的上下两边多余部分进行切除,从而保留关键的图像部位,能够大幅度提高识别率。
element_object = browser.find_element_by_xpath("xpath_element")
px = element_object.value_of_css_property("top")
接下来就要对图像进行灰度处理:
import numpy
import cv2
def make_threshold(img):
"""全局阈值
将图片二值化,去除噪点,让其黑白分明"""
x = numpy.ones(img.shape, numpy.uint8) * 255
y = img - x
result, thresh = cv2.threshold(y, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
# 将二值化后的结果返回
return thresh
class ComputeDistance:
"""获取需要滑动的距离
将验证码背景大图和需要滑动的小图进行处理,先在大图中找到相似的小图位置,再获取对应的像素偏移量"""
def __init__(self, Background_path: str, image_to_move: str, offset_top_px: int):
"""
:param Background_path: 验证码背景大图
:param image_to_move: 需要滑动的小图
:param offset_top_px: 小图距离在大图上的顶部边距(像素偏移量)
"""
self.Background_img = cv2.imread(Background_path)
self.offset_px = offset_top_px
self.show_img = show_img
small_img_data = cv2.imread(image_to_move, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
# 得到一个改变维度为50的乘以值
scaleX = 50 / small_img_data.shape[1]
# 使用最近邻插值法缩放,让xy乘以scaleX,得到缩放后shape为50x50的图片
self.tpl_img = cv2.resize(small_img_data, (0, 0), fx=scaleX, fy=scaleX)
self.Background_cutting = None
def tpl_op(self):
# 将小图转换为灰色
tpl_gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.tpl_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
h, w = tpl_gray.shape
# 将背景图转换为灰色
# Background_gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.Background_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
Background_gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.Background_cutting, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 得到二值化后的小图
threshold_img = make_threshold(tpl_gray)
# 将小图与大图进行模板匹配,找到所对应的位置
result = cv2.matchTemplate(Background_gray, threshold_img, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
# 左上角位置
top_left = (max_loc[0] - 5, max_loc[1] + self.offset_px)
# 右下角位置
bottom_right = (top_left[0] + w, top_left[1] + h)
# 在源颜色大图中画出小图需要移动到的终点位置
"""rectangle(图片源数据, 左上角, 右下角, 颜色, 画笔厚度)"""
cv2.rectangle(self.Background_img, top_left, bottom_right, (0, 0, 255), 2)
def cutting_background(self):
"""切割图片的上下边框"""
height = self.tpl_img.shape[0]
# 将大图中上下多余部分去除,如: Background_img[40:110, :]
self.Background_cutting = self.Background_img[self.offset_px - 10: self.offset_px + height + 10, :]
def run(self):
# 如果小图的长度与大图的长度一致则不用将大图进行切割,可以将self.cutting_background()注释掉
self.cutting_background()
return self.tpl_op()
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_path1 = "背景图路径"
image_path2 = "小图路径"
distance_px = "像素距离"
main = ComputeDistance(image_path1, image_path2, distance_px)
main.run()
上面代码可以返回小图到凹点的距离,现在我们可以看一下灰度处理中的图片样子:

得到距离后还要对这个距离数字进行处理一下,要让它拆分成若干个小数,这么做的目的是在拖动的时候不能一下拖动到终点,
要模仿人类的手速缓缓向前行驶,不然很明显是机器在操控。
比如到终点的距离为100,那么要把它转为 [8, 6, 11, 10, 3, 6, 3, -2, 4, 0, 15, 1, 9, 6, -2, 4, 1, -2, 15, 6, -2] 类似的,列表中的数加起来正好为100.
最简单的转换:
def handle_distance(distance):
"""将直线距离转为缓慢的轨迹"""
import random
slow_distance = []
while sum(slow_distance) <= distance:
slow_distance.append(random.randint(-2, 15))
if sum(slow_distance) != distance:
slow_distance.append(distance - sum(slow_distance))
return slow_distance
有了到终点的距离,接下来就开始拖动吧:
import time
from random import randint
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
def move_slider(website, slider, track, **kwargs):
"""将滑块移动到终点位置
:param website: selenium页面对象
:param slider: selenium页面中滑块元素对象
:param track: 到终点所需的距离
"""
name = kwargs.get('name', '滑块')
try:
if track[0] > 200:
return track[0]
# 点击滑块元素并拖拽
ActionChains(website).click_and_hold(slider).perform()
time.sleep(0.15)
for i in track:
# 随机上下浮动鼠标
ActionChains(website).move_by_offset(xoffset=i, yoffset=randint(-2, 2)).perform()
# 释放元素
time.sleep(1)
ActionChains(website).release(slider).perform()
time.sleep(1)
# 随机拿开鼠标
ActionChains(website).move_by_offset(xoffset=randint(200, 300), yoffset=randint(200, 300)).perform()
print(f'[网页] 拖拽 {name}')
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f'[网页] 拖拽 {name} 失败 {e}')
教程结束,让我们结合上面代码做一个案例吧。
访问今日头条某博主的主页,直接打开主页的链接会出现验证码。
下面代码 使用pip安装好相关依赖库后可直接运行:
调用ComputeDistance类时,参数 show_img=True 可以在拖动验证码前进行展示背景图识别终点后的区域在哪里, 如:
distance_obj = ComputeDistance(background_path, small_path, px, show_img=True)
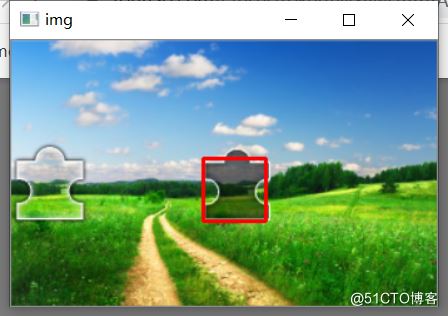
OK,下面为案例代码:
import os
import time
import requests
import cv2
import numpy
from random import randint
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
def show_image(img_array, name='img', resize_flag=False):
"""展示图片"""
maxHeight = 540
maxWidth = 960
scaleX = maxWidth / img_array.shape[1]
scaleY = maxHeight / img_array.shape[0]
scale = min(scaleX, scaleY)
if resize_flag and scale < 1:
img_array = cv2.resize(img_array, (0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale)
cv2.imshow(name, img_array)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyWindow(name)
def make_threshold(img):
"""全局阈值
将图片二值化,去除噪点,让其黑白分明"""
x = numpy.ones(img.shape, numpy.uint8) * 255
y = img - x
result, thresh = cv2.threshold(y, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
# 将二值化后的结果返回
return thresh
def move_slider(website, slider, track, **kwargs):
"""将滑块移动到终点位置
:param website: selenium页面对象
:param slider: selenium页面中滑块元素对象
:param track: 到终点所需的距离
"""
name = kwargs.get('name', '滑块')
try:
if track[0] > 200:
return track[0]
# 点击滑块元素并拖拽
ActionChains(website).click_and_hold(slider).perform()
time.sleep(0.15)
for i in track:
# 随机上下浮动鼠标
ActionChains(website).move_by_offset(xoffset=i, yoffset=randint(-2, 2)).perform()
# 释放元素
time.sleep(1)
ActionChains(website).release(slider).perform()
time.sleep(1)
# 随机拿开鼠标
ActionChains(website).move_by_offset(xoffset=randint(200, 300), yoffset=randint(200, 300)).perform()
print(f'[网页] 拖拽 {name}')
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f'[网页] 拖拽 {name} 失败 {e}')
class ComputeDistance:
"""获取需要滑动的距离
将验证码背景大图和需要滑动的小图进行处理,先在大图中找到相似的小图位置,再获取对应的像素偏移量"""
def __init__(self, Background_path: str, image_to_move: str, offset_top_px: int, show_img=False):
"""
:param Background_path: 验证码背景大图
:param image_to_move: 需要滑动的小图
:param offset_top_px: 小图距离在大图上的顶部边距(像素偏移量)
:param show_img: 是否展示图片
"""
self.Background_img = cv2.imread(Background_path)
self.offset_px = offset_top_px
self.show_img = show_img
small_img_data = cv2.imread(image_to_move, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
# 得到一个改变维度为50的乘以值
scaleX = 50 / small_img_data.shape[1]
# 使用最近邻插值法缩放,让xy乘以scaleX,得到缩放后shape为50x50的图片
self.tpl_img = cv2.resize(small_img_data, (0, 0), fx=scaleX, fy=scaleX)
self.Background_cutting = None
def show(self, img):
if self.show_img:
show_image(img)
def tpl_op(self):
# 将小图转换为灰色
tpl_gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.tpl_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
h, w = tpl_gray.shape
# 将背景图转换为灰色
# Background_gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.Background_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
Background_gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.Background_cutting, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 得到二值化后的小图
threshold_img = make_threshold(tpl_gray)
# 将小图与大图进行模板匹配,找到所对应的位置
result = cv2.matchTemplate(Background_gray, threshold_img, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
# 左上角位置
top_left = (max_loc[0] - 5, max_loc[1] + self.offset_px)
# 右下角位置
bottom_right = (top_left[0] + w, top_left[1] + h)
# 在源颜色大图中画出小图需要移动到的终点位置
"""rectangle(图片源数据, 左上角, 右下角, 颜色, 画笔厚度)"""
cv2.rectangle(self.Background_img, top_left, bottom_right, (0, 0, 255), 2)
if self.show_img:
show_image(self.Background_img)
return top_left
def cutting_background(self):
"""切割图片的上下边框"""
height = self.tpl_img.shape[0]
# 将大图中上下多余部分去除,如: Background_img[40:110, :]
self.Background_cutting = self.Background_img[self.offset_px - 10: self.offset_px + height + 10, :]
def run(self):
# 如果小图的长度与大图的长度一致则不用将大图进行切割,可以将self.cutting_background()注释掉
self.cutting_background()
return self.tpl_op()
class TodayNews(object):
def __init__(self):
self.url = "https://www.toutiao.com/c/user/token/" \
"MS4wLjABAAAA4EKNlqVeNTTuEdWn0VytNS8cdODKTsNNwLTxOnigzZtclro2Kylvway5mTyTUKvz/"
self.process_folder = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), "Desktop", "today_news")
self.background_path = os.path.join(self.process_folder, "background.png")
self.small_path = os.path.join(self.process_folder, "small.png")
self.small_px = None
self.xpath = {}
self.browser = None
def check_file_exist(self):
"""检查流程目录是否存在"""
if not os.path.isdir(self.process_folder):
os.mkdir(self.process_folder)
def start_browser(self):
"""启动浏览器"""
self.browser = webdriver.Chrome()
self.browser.maximize_window()
def close_browser(self):
self.browser.quit()
def wait_element_loaded(self, xpath: str, timeout=10, close_browser=True):
"""等待页面元素加载完成
:param xpath: xpath表达式
:param timeout: 最长等待超时时间
:param close_browser: 元素等待超时后是否关闭浏览器
:return: Boolean
"""
now_time = int(time.time())
while int(time.time()) - now_time < timeout:
# noinspection PyBroadException
try:
element = self.browser.find_element_by_xpath(xpath)
if element:
return True
time.sleep(1)
except Exception:
pass
else:
if close_browser:
self.close_browser()
# print("查找页面元素失败,如果不存在网络问题请尝试修改xpath表达式")
return False
def add_page_element(self):
self.xpath['background_img'] = '//div[@role="dialog"]/div[2]/img[1]'
self.xpath['small_img'] = '//div[@role="dialog"]/div[2]/img[2]'
self.xpath['slider_button'] = '//div[@id="secsdk-captcha-drag-wrapper"]/div[2]'
def process_main(self):
"""处理页面内容"""
self.browser.get(self.url)
for _ in range(10):
if self.wait_element_loaded(self.xpath['background_img'], timeout=5, close_browser=False):
time.sleep(1)
# 截图
self.browser.find_element_by_xpath(self.xpath['background_img']).screenshot(self.background_path)
small_img = self.browser.find_element_by_xpath(self.xpath['small_img'])
# 获取小图片的URL链接
small_url = small_img.get_attribute("src")
# 获取小图片距离背景图顶部的像素距离
self.small_px = small_img.value_of_css_property("top").replace("px", "").split(".")[0]
response = requests.get(small_url)
if response.ok:
with open(self.small_path, "wb") as file:
file.write(response.content)
time.sleep(1)
# 如果没滑动成功则刷新页面重试
if not self.process_slider():
self.browser.refresh()
continue
else:
break
@staticmethod
def handle_distance(distance):
"""将直线距离转为缓慢的轨迹"""
import random
slow_distance = []
while sum(slow_distance) <= distance:
slow_distance.append(random.randint(-2, 15))
if sum(slow_distance) != distance:
slow_distance.append(distance - sum(slow_distance))
return slow_distance
def process_slider(self):
"""处理滑块验证码"""
distance_obj = ComputeDistance(self.background_path, self.small_path, int(self.small_px), show_img=False)
# 获取移动所需的距离
distance = distance_obj.run()
track = self.handle_distance(distance[0])
track.append(-2)
slider_element = self.browser.find_element_by_xpath(self.xpath['slider_button'])
move_slider(self.browser, slider_element, track)
time.sleep(2)
# 如果滑动完成则返回True
if not self.wait_element_loaded(self.xpath['slider_button'], timeout=2, close_browser=False):
return True
else:
return False
def run(self):
self.check_file_exist()
self.start_browser()
self.add_page_element()
self.process_main()
# self.close_browser()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main = TodayNews()
main.run()
到此这篇关于OpenCV结合selenium实现滑块验证码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关OpenCV selenium滑块验证码内容请搜索hwidc以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持hwidc!
【本文由:http://www.yidunidc.com/mgzq.html复制请保留原URL】