Python常用配置文件ini、json、yaml读写总结
本文参考文章,出于学习目的,写本文。
开发项目时,为了维护一些经常需要变更的数据,比如数据库的连接信息、请求的url、测试数据等,需要将这些数据写入配置文件,将数据和代码分离,只需要修改配置文件的参数,就可以快速完成环境的切换或者测试数据的更新,常用的配置文件格式有ini、json、yaml等,下面简单给大家介绍下,Python如何读写这几种格式的文件。
1、ini格式
ini 即 Initialize ,是Windows中常用的配置文件格式,结构比较简单,主要由节(Section)、键(key)和值(value)组成。每个独立部分称之为section,每个section内,都是key(option)=value形成的键值对。
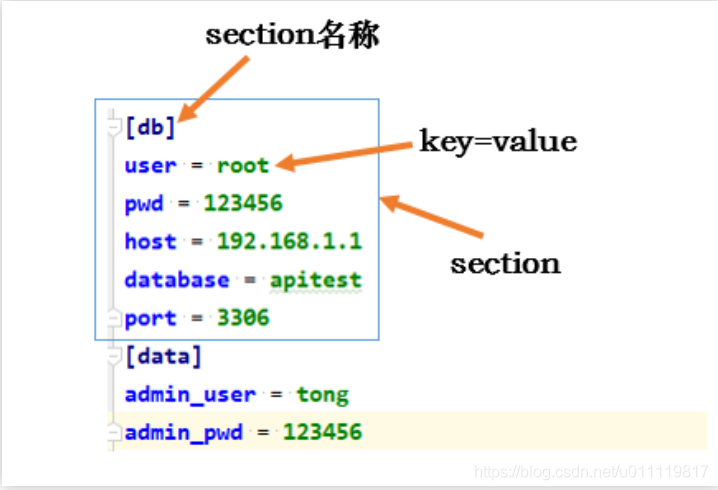
在Python3中,使用自带的configparser库(配置文件解析器)来解析类似于ini这种格式的文件,比如config、conf。
可以看到,ini只有字典一种格式,且全部都是字符串。
1.1 ini的读取删除操作
import configparser
#使用前,需要创建一个实例
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
#读取并打开文件
config.read('test.ini',encoding='utf-8')
#获取sections,返回列表
print(config.sections())
#[db,data]
#获取sections下的所有options
print(config.options('db'))
#['user', 'pwd', 'host', 'database', 'port']
#获取指定section下指定的options
print(config.get('db','user'))
# root
#获取section中所有键值对
print(config.items('data'))
#[('admin_user', 'tong'), ('admin_pwd', '123456')]
#删除整个section
config.remove_section('data')
#删除某个section下的key
config.remove_option('db','host')
print(config.items('db'))
1.2 ini 写入操作
写入操作可能会比较少
import configparser
config=configparser.ConfigParser()
config['url']={'url':'www.baidu.com'} #类似于字典操作
with open('example.ini','w') as configfile:
config.write(configfile)

2.JSON格式
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,这些特性使json成为理想的数据交换语言,易于阅读和编写,同时易于机器解析和生成。
2.1 JSON示例格式
{
"name":"smith",
"age":30,
"sex":"男"
}
Python中使用内置模块json操作json数据,使用json.load()和json.dump方法进行json格式文件读写:
# 读取json
import json
with open('test1.json') as f:
a = json.load(f)
print(a)
# 写入json
import json
dic ={
"name" : "xiaoming",
"age" : 20,
"phonenumber" : "15555555555"
}
with open("test2.json", "w") as outfile:
json.dump(dic, outfile)
有关json更多的介绍请看链接
3. yaml格式
yaml全称Yet Another Markup Language(另一种标记语言),它是一种简洁的非标记语言,以数据为中心,使用空格,缩进,分行组织数据,解析成本很低,是非常流行的配置文件语言。
3.1 yaml的语法特点
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
- 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。
- 字符串不需要使用引号标注,但若字符串包含有特殊字符则需用引号标注
- 注释标识为#
3.2 yaml示例
case1: info: title: "正常登陆" url: http://192.168.1.1/user/login method: "POST" json: username: "admin" password: "123456" expected: status_code: - 200 - 300 content: "user_id"
读取后效果:

yaml支持的数据结构有三种
- 对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/ 哈希(hashes) / 字典(dictionary)
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence) / 列表(list)
- 纯量(scalars):单个的、不可再分的值。字符串、布尔值、整数、浮点数、Null、时间、日期
Python中使用pyyaml处理yaml格式数据
使用前,需要进行安装:
pip install pyyaml
3.3 yaml文件读取
用python读取yaml文件,先用open方法读取文件数据,再通过load方法转成字典。
import yaml
with open("testyaml.yaml", encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = yaml.safe_load(file)
print(data)
print(data['case1']['json'])
print(data['case1']['json']['username'])
3.4 yaml文件的写入
import yaml
#定义一个字典
content = {
'id': 1,
'text': 'programming languages',
'members': ['java', 'python', 'python', 'c', 'go', 'shell'],
'next': {'a':1,'b':2}
}
with open('test3.yaml', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
yaml.dump(content, file, default_flow_style=False, encoding='utf-8', allow_unicode=True)
以上有三种数据类型,写入文件效果为:
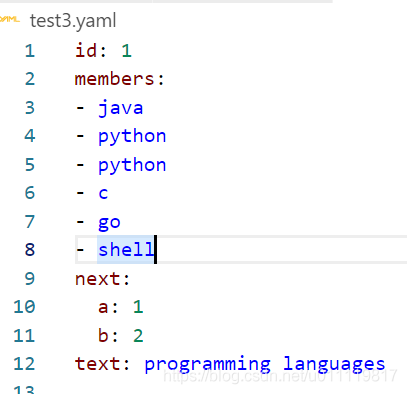
当然手动写也没有问题。
到此这篇关于Python常用配置文件ini、json、yaml读写总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python读写ini、json、yaml配置文件内容请搜索hwidc以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持hwidc!
【文章出处:http://www.1234xp.com/hggf.html欢迎留下您的宝贵建议】