kotlin实现五子棋单机游戏
最近学了点kotlin的相关知识,顺手写了一个简单的五子棋单机游戏,分享给大家吧!有兴趣的可以看看
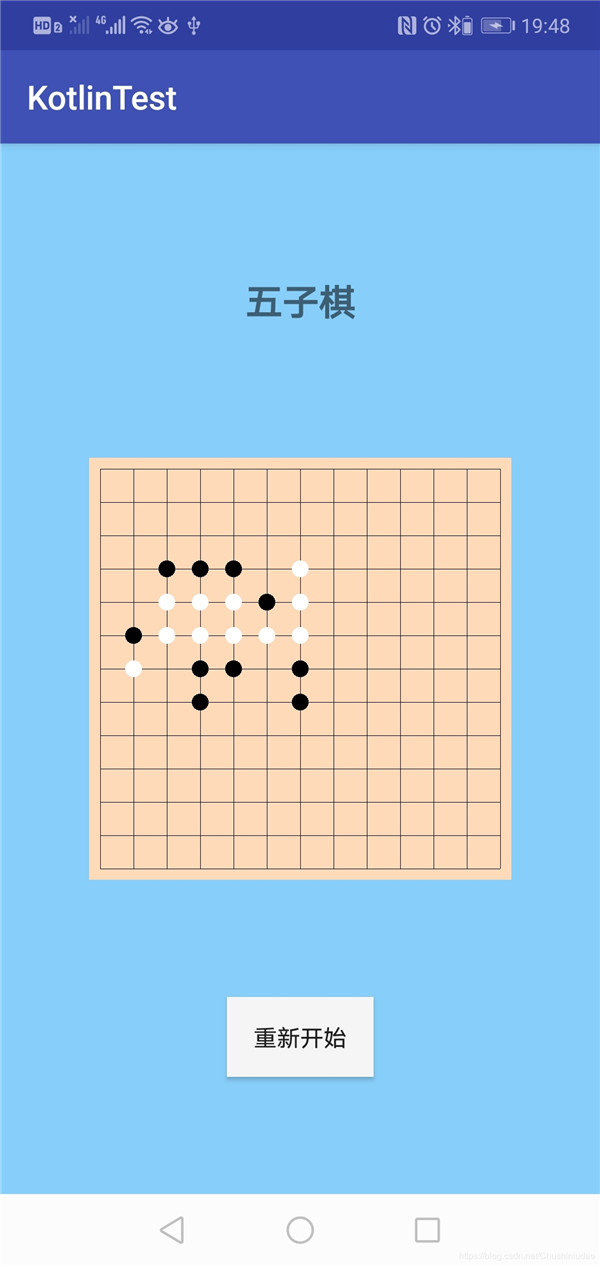
五子棋界面
package wjc.kotlintest
import android.content.Context
import android.graphics.Canvas
import android.graphics.Color
import android.graphics.Paint
import android.util.AttributeSet
import android.view.View
/**
* Created by wjc on 2019/12/9.
*/
class MyCustomView : View {
var paint: Paint = Paint()
var paintWhite: Paint = Paint()
var paintBlack: Paint = Paint()
val H: Int = 12
val V: Int = 12
var list = arrayListOf<Data>()//白子和黑子
var listW = arrayListOf<Data>()//白子
var listB = arrayListOf<Data>()//黑子
var wSuccess: Boolean = false //白旗获胜标志
var bSuccess: Boolean = false //黑棋获胜标志
init {
paintWhite.color = Color.WHITE
paintWhite.style = Paint.Style.FILL
paintBlack.color = Color.BLACK
paintBlack.style = Paint.Style.FILL
}
constructor(context: Context) : this(context, null)
constructor(context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attr, 0)
constructor(context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : super(context, attr, defStyleAttr)
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
val widthMode: Int = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec)
val widthSize: Int = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
val heightMode: Int = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec)
val heightSize: Int = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(760, 760)
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(760, heightSize)
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, 760)
}
}
override fun draw(canvas: Canvas?) {
super.draw(canvas)
for (i in 0..H) {
canvas!!.drawLine(20f, 20f + 60 * i, 740f, 20f + 60 * i, paint)
}
for (j in 0..V) {
canvas!!.drawLine(20f + 60 * j, 20f, 20f + 60 * j, 740f, paint)
}
if (listW.size != 0) {
for (item in listW) {
canvas!!.drawCircle(item.point.x * 60 + 20f, item.point.y * 60 + 20f, 15f, paintWhite)
}
}
if (listB.size != 0) {
for (item in listB) {
canvas!!.drawCircle(item.point.x * 60 + 20f, item.point.y * 60 + 20f, 15f, paintBlack)
}
}
}
fun addData(data: Data) {
if (list.size == 0) {
list.add(data)
listW.add(data)
return
}
if (!select(data)) {
list.add(data)
if (listW.size == listB.size) {
//白旗是否获胜
wSuccess = isSuccess(data, listW)
//白旗走
listW.add(data)
} else {
//黑棋是否获胜
bSuccess = isSuccess(data, listB)
//黑棋走
listB.add(data)
}
}
}
fun select(data: Data): Boolean {
for (item in list) {
if (data.equals(item))
return true
}
return false
}
fun isSuccess(data: Data, arry: List<Data>): Boolean {
return horizontalErgodic(data, arry) || verticalErgodic(data, arry) || acrossErgodic(data, arry)
}
//横向遍历
fun horizontalErgodic(data: Data, arry: List<Data>): Boolean {
//记录连续的棋子数,凑成5个即一方获胜
var rn = 0
var ln = 0
//向右遍历,y相同,x递增
for (i in 1..5) {
var _rn: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.y == item.point.y) {
if (data.point.x + i == item.point.x) {
rn++
break
}
}
}
if (_rn != rn) {
break
}
}
//一方获胜,游戏结束
if (rn == 4) {
return true
}
//向左遍历,y相同,x递减
for (i in 1..5) {
var _ln: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.y == item.point.y && data.point.x - i == item.point.x) {
ln++
break
}
}
if (_ln != ln) {
break
}
}
//一方获胜,游戏结束
if (ln == 4) {
return true
}
//向左向右
return ln + rn >= 4
}
//纵向遍历
fun verticalErgodic(data: Data, arry: List<Data>): Boolean {
//记录连续的棋子数,凑成5个即一方获胜
var tn = 0
var bn = 0
//向上遍历,x相同,y递增
for (i in 1..5) {
val _tn: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.x == item.point.x && data.point.y + i == item.point.y) {
tn++
break
}
}
if (_tn != tn) {
break
}
}
//一方获胜,游戏结束
if (tn == 4) {
return true
}
//向下遍历,x相同,y递减
for (i in 1..5) {
val _bn: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.x == item.point.x && data.point.y - i == item.point.y) {
bn++
break
}
}
if (_bn != bn) {
break
}
}
if (bn == 4) {
return true
}
//向左向右
return bn + tn >= 4
}
//对角遍历
fun acrossErgodic(data: Data, arry: List<Data>): Boolean {
var lt = 0 //左上方向连续棋子个数
var lb = 0 //左下方向连续棋子个数
var rt = 0 //右上方向连续棋子个数
var rb = 0 //右下方向连续棋子个数
//右下方向遍历
for (i in 1..5) {
val _rb: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.x + i == item.point.x && data.point.y + i == item.point.y) {
rb++
break
}
}
if (_rb != rb) {
break
}
}
if (rb == 4) {
return true
}
//左上方向遍历
for (i in 1..5) {
val _lt: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.x - i == item.point.x && data.point.y - i == item.point.y) {
lt++
break
}
}
if (_lt != lt) {
break
}
}
if (lt == 4) {
return true
}
//左上右下这条对角线
if (lt + rb >= 4) {
return true
}
//右上遍历
for (i in 1..5) {
val _rt: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.x + i == item.point.x && data.point.y - i == item.point.y) {
rt++
break
}
}
if (_rt != rt) {
break
}
}
if (rt == 4) {
return true
}
//左下遍历
for (i in 1..5) {
val _lb: Int = i
for (item in arry) {
if (data.point.x - i == item.point.x && data.point.y + i == item.point.y) {
lb++
break
}
}
if (_lb != lb) {
break
}
}
if (lb == 4) {
return true
}
//左下右上这条对角线
return lb + rt >= 4
}
fun reset() {
list.clear()
listW.clear()
listB.clear()
wSuccess = false
bSuccess = false
}
}
主界面
package wjc.kotlintest
import android.graphics.Point
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.MotionEvent
import android.widget.Toast
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
custom_view.setOnTouchListener { v, e ->
when (e.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
val x = e.x
val y = e.y
val x_n: Int = ((x - 20) / 60f + 0.5f).toInt()
val y_n: Int = ((y - 20) / 60f + 0.5f).toInt()
val data = Data(Point(x_n, y_n))
custom_view.addData(data)
custom_view.invalidate()
if (custom_view.wSuccess) {
Toast.makeText(this, "白旗获胜!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
custom_view.setEnabled(false)
} else if (custom_view.bSuccess) {
Toast.makeText(this, "黑棋获胜!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
custom_view.setEnabled(false)
}
}
}
return@setOnTouchListener true
}
reset.setOnClickListener {
custom_view.reset()
custom_view.invalidate()
custom_view.setEnabled(true)
}
}
}
数据类
package wjc.kotlintest
import android.graphics.Point
/**
* Created by wjc on 2019/12/10.
*/
data class Data(val point: Point) {
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
if (other is Data) {
if (point.x == other.point.x && point.y == other.point.y) {
return true
} else {
return false
}
} else {
return false
}
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持海外IDC网。
