linux 中断号是什么意思
linux中断号是系统分配给每个中断源的代号,以便识别和处理;在采用向量中断方式的中断系统中,CPU必须通过它才可以找到中断服务程序的入口地址,实现程序的转移。

本教程操作环境:linux5.9.8系统、Dell G3电脑。
linux 中断号是什么意思?
中断号与中断编程:
1、中断号
中断号是系统分配给每个中断源的代号,以便识别和处理。在采用向量中断方式的中断系统中,CPU必须通过它才可以找到中断服务程序的入口地址,实现程序的转移。
在ARM裸机中实现中断需要配置:
I/O口为中断模式,触发方式,I/O口中断使能 设置GIC中断使能,分发配置,分发总使能,CPU外部中断接口使能,中断优先级登录后复制
在linux内核中实现中断,只需要知道:
中断号是什么,怎么得到中断号 中断处理方法登录后复制
2、获取中断号的方法:
/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-fs4412.dts登录后复制
1)看原理图,芯片手册找到中断源对应的中断号SPI Port No
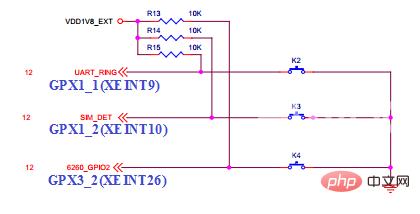

2)进入设备树,在arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4x12-pinctrl.dtsi中
gpx1: gpx1 {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
interrupt-controller; //中断控制器
interrupt-parent = <&gic>; //继承于gic
interrupts = <0 24 0>, <0 25 0>, <0 26 0>, <0 27 0>,
<0 28 0>, <0 29 0>, <0 30 0>, <0 31 0>;
#interrupt-cells = <2>; //子继承的interrupts的长度
};登录后复制括号中的24、 25等对应于SPI Port No,以上是系统中已经定义好的节点
在编程中,需要定义自己的节点,用来描述按键,打开可编辑的设备树文件:
arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-fs4412.dts,进入文件。
3)定义节点,描述当前设备用的中断号
1 key_int_node{
2 compatible = "test_key";
3 interrupt-parent = <&gpx1>; //继承于gpx1
4 interrupts = <2 4>; //2表示第几个中断号,4表示触发方式为下降沿5 }; //interrupts里长度由父母的-cell决定登录后复制再举个栗子,设置k4 --- GPX3_2(XEINT26) 的节点,中断号
1 key_int_node{
2 compatible = "test_key";
3 interrupt-parent = <&gpx3>; //继承于gpx3
4 interrupts = <2 4>; //2表示第2个中断号,4表示触发方式为下降沿
5 };登录后复制
中断号的定位方法:
看I/O引脚,GPX1_2,中断号就是GPX1里面的第2个
4)编译设备树:make dtbs
更新设备树文件: cp -raf arch/arm/boot/dts/exynos4412-fs4412.dtb /tftpboot/
查看定义的节点:在根目录的 proc/device-tree/目录下
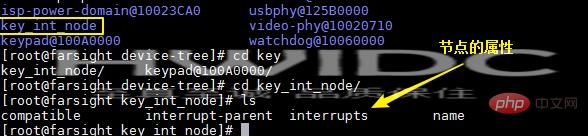
3、实现中断处理方法
在驱动中通过代码获取到中断号,并且申请中断
先看一下中断相关的函数:
1 a,获取到中断号码:
2 int get_irqno_from_node(void)
3 {
4 // 获取到设备树中的节点
5 struct device_node *np = of_find_node_by_path("/key_int_node");
6 if(np){
7 printk("find node ok\n");
8 }else{
9 printk("find node failed\n");
10 }
11
12 // 通过节点去获取到中断号码
13 int irqno = irq_of_parse_and_map(np, 0);
14 printk("irqno = %d\n", irqno);
15
16 return irqno;
17 }
18 b,申请中断
19 int request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags, const char * name, void * dev)
20 参数1: irq 设备对应的中断号
21 参数2: handler 中断的处理函数
22 typedef irqreturn_t (*irq_handler_t)(int, void *);
23 参数3:flags 触发方式
24 #define IRQF_TRIGGER_NONE 0x00000000 //内部控制器触发中断的时候的标志
25 #define IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING 0x00000001 //上升沿
26 #define IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING 0x00000002 //下降沿
27 #define IRQF_TRIGGER_HIGH 0x00000004 // 高点平
28 #define IRQF_TRIGGER_LOW 0x00000008 //低电平触发
29 参数4:name 中断的描述,自定义,主要是给用户查看的
30 /proc/interrupts
31 参数5:dev 传递给参数2中函数指针的值
32 返回值: 正确为0,错误非0
33
34
35 参数2的赋值:即中断处理函数
36 irqreturn_t key_irq_handler(int irqno, void *devid)
37 {
38 return IRQ_HANDLED;
39 }
43
44 c, 释放中断:
45 void free_irq(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id)
46 参数1: 设备对应的中断号
47 参数2:与request_irq中第5个参数保持一致登录后复制代码实现获取中断号,并注册中断,按下按键引发中断,打印信息
1 #include <linux/init.h>
2 #include <linux/module.h>
3 #include <linux/fs.h>
4 #include <linux/device.h>
5 #include <asm/uaccess.h>
6 #include <asm/io.h>
7 #include <linux/slab.h>
8 #include <linux/of.h>
9 #include <linux/of_irq.h>
10 #include <linux/interrupt.h>
11
12 int irqno; //中断号
13
14
15 irqreturn_t key_irq_handler(int irqno, void *devid)
16 {
17 printk("----------%s---------",__FUNCTION__);
18 return IRQ_HANDLED;
19 }
20
21
22 //获取中断号
23 int get_irqno_from_node(void)
24 {
25 //获取设备树中的节点
26 struct device_node *np = of_find_node_by_path("/key_int_node");
27 if(np){
28 printk("find node success\n");
29 }else{
30 printk("find node failed\n");
31 }
32
33 //通过节点去获取中断号
34 int irqno = irq_of_parse_and_map(np, 0);
35 printk("iqrno = %d",irqno);
36
37 return irqno;
38 }
39
40
41
42 static int __init key_drv_init(void)
43 {
44 //演示如何获取到中断号
45 int ret;
46
47 irqno = get_irqno_from_node();
48
49 ret = request_irq(irqno, key_irq_handler, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING | IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING,
50 "key3_eint10", NULL);
51 if(ret != 0)
52 {
53 printk("request_irq error\n");
54 return ret;
55 }
56
57 return 0;
58 }
59
60 static void __exit key_drv_exit(void)
61 {
62 free_irq(irqno, NULL); //free_irq与request_irq的最后一个参数一致
63 }
64
65
66
67 module_init(key_drv_init);
68 module_exit(key_drv_exit);
69
70 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
key_drv.c登录后复制key_drv.c测试效果:
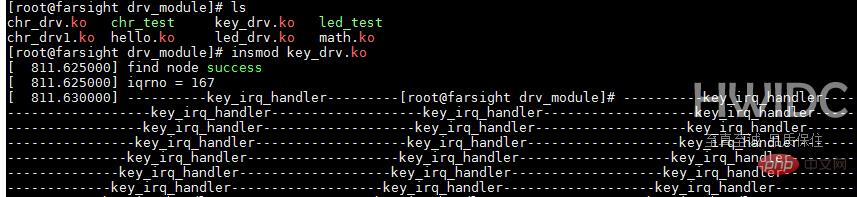
按键按下,打印信息,但出现了按键抖动
cat /proc/interrupt

4、 中断编程 --- 字符设备驱动框架
// 1,设定一个全局的设备对象
key_dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct key_desc), GFP_KERNEL);
// 2,申请主设备号
key_dev->dev_major = register_chrdev(0, "key_drv", &key_fops);
// 3,创建设备节点文件
key_dev->cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "key_cls");
key_dev->dev = device_create(key_dev->cls, NULL, MKDEV(key_dev->dev_major,0), NULL, "key0");
// 4,硬件初始化:
a.地址映射
b.中断申请登录后复制5、驱动实现将硬件所产生的数据传递给用户
1)硬件如何获取数据
key: 按下和抬起: 1/0读取key对应的gpio的状态,可以判断按下还是抬起
读取key对应gpio的寄存器--数据寄存器
//读取数据寄存器int value = readl(key_dev->reg_base + 4) & (1<<2);登录后复制2)驱动传递数据给用户
在中断处理中填充数据:
key_dev->event.code = KEY_ENTER;
key_dev->event.value = 0;
在xxx_read中奖数据传递给用户
ret = copy_to_user(buf, &key_dev->event, count);登录后复制3)用户获取数据
while(1)
{
read(fd, &event, sizeof(struct key_event)); if(event.code == KEY_ENTER)
{ if(event.value)
{
printf("APP__ key enter pressed\n");
}else{
printf("APP__ key enter up\n");
}
}
}登录后复制6、示例:
1 #include <linux/init.h>
2 #include <linux/module.h>
3 #include <linux/of.h>
4 #include <linux/of_irq.h>
5 #include <linux/interrupt.h>
6 #include <linux/slab.h>
7 #include <linux/fs.h>
8 #include <linux/device.h>
9 #include <linux/kdev_t.h>
10 #include <linux/err.h>
11 #include <linux/device.h>
12 #include <asm/io.h>
13 #include <asm/uaccess.h>
14
15
16 #define GPXCON_REG 0X11000C20 //不可以从数据寄存器开始映射,要配置寄存器
17 #define KEY_ENTER 28
18
19 //0、设计一个描述按键的数据的对象
20 struct key_event{
21 int code; //按键类型:home,esc,enter
22 int value; //表状态,按下,松开
23 };
24
25 //1、设计一个全局对象——— 描述key的信息
26 struct key_desc{
27 unsigned int dev_major;
28 int irqno; //中断号
29 struct class *cls;
30 struct device *dev;
31 void *reg_base;
32 struct key_event event;
33 };
34
35 struct key_desc *key_dev;
36
37
38 irqreturn_t key_irq_handler(int irqno, void *devid)
39 {
40 printk("----------%s---------",__FUNCTION__);
41
42 int value;
43 //读取按键状态
44 value = readl(key_dev->reg_base + 4) & (0x01<<2);
45
46 if(value){
47 printk("key3 up\n");
48 key_dev->event.code = KEY_ENTER;
49 key_dev->event.value = 0;
50 }else{
51 printk("key3 down\n");
52 key_dev->event.code = KEY_ENTER;
53 key_dev->event.value = 1;
54 }
55 return IRQ_HANDLED;
56 }
57
58
59 //获取中断号
60 int get_irqno_from_node(void)
61 {
62 int irqno;
63 //获取设备树中的节点
64 struct device_node *np = of_find_node_by_path("/key_int_node");
65 if(np){
66 printk("find node success\n");
67 }else{
68 printk("find node failed\n");
69 }
70
71 //通过节点去获取中断号
72 irqno = irq_of_parse_and_map(np, 0);
73 printk("iqrno = %d",key_dev->irqno);
74
75 return irqno;
76 }
77
78 ssize_t key_drv_read (struct file * filp, char __user * buf, size_t count, loff_t * fops)
79 {
80 //printk("----------%s---------",__FUNCTION__);
81 int ret;
82 ret = copy_to_user(buf, &key_dev->event, count);
83 if(ret > 0)
84 {
85 printk("copy_to_user error\n");
86 return -EFAULT;
87 }
88
89 //传递给用户数据后,将数据清除,否则APP每次读都是第一次的数据
90 memset(&key_dev->event, 0, sizeof(key_dev->event));
91 return count;
92 }
93
94 ssize_t key_drv_write (struct file *filp, const char __user * buf, size_t count, loff_t * fops)
95 {
96 printk("----------%s---------",__FUNCTION__);
97 return 0;
98 }
99
100 int key_drv_open (struct inode * inode, struct file *filp)
101 {
102 printk("----------%s---------",__FUNCTION__);
103 return 0;
104 }
105
106 int key_drv_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
107 {
108 printk("----------%s---------",__FUNCTION__);
109 return 0;
110 }
111
112
113 const struct file_operations key_fops = {
114 .open = key_drv_open,
115 .read = key_drv_read,
116 .write = key_drv_write,
117 .release = key_drv_close,
118
119 };
120
121
122
123 static int __init key_drv_init(void)
124 {
125 //演示如何获取到中断号
126 int ret;
127
128 //1、设定全局设备对象并分配空间
129 key_dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct key_desc), GFP_KERNEL); //GFP_KERNEL表正常分配内存
130 //kzalloc相比于kmalloc,不仅分配连续空间,还会将内存初始化清零
131
132 //2、动态申请设备号
133 key_dev->dev_major = register_chrdev(0, "key_drv", &key_fops);
134
135 //3、创建设备节点文件
136 key_dev->cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "key_cls");
137 key_dev->dev = device_create(key_dev->cls, NULL, MKDEV(key_dev->dev_major, 0), NULL, "key0");
138
139 //4、硬件初始化 -- 地址映射或中断申请
140
141 key_dev->reg_base = ioremap(GPXCON_REG,8);
142
143 key_dev->irqno = get_irqno_from_node();
144
145 ret = request_irq(key_dev->irqno, key_irq_handler, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING | IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING,
146 "key3_eint10", NULL);
147 if(ret != 0)
148 {
149 printk("request_irq error\n");
150 return ret;
151 }
152
153 //a. 硬件如何获取数据
154
155
156
157 return 0;
158 }
159
160 static void __exit key_drv_exit(void)
161 {
162 iounmap(GPXCON_REG);
163 free_irq(key_dev->irqno, NULL); //free_irq与request_irq的最后一个参数一致
164 device_destroy(key_dev->cls, MKDEV(key_dev->dev_major, 0));
165 class_destroy(key_dev->cls);
166 unregister_chrdev(key_dev->dev_major, "key_drv");
167 kfree(key_dev);
168 }
169
170
171
172 module_init(key_drv_init);
173 module_exit(key_drv_exit);
174
175 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
key_drv.c登录后复制key_drv.c1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 #include <stdlib.h>
4 #include <unistd.h>
5 #include <sys/types.h>
6 #include <sys/stat.h>
7 #include <fcntl.h>
8
9
10 #define KEY_ENTER 28
11
12 //0、设计一个描述按键的数据的对象
13 struct key_event{
14 int code; //按键类型:home,esc,enter
15 int value; //表状态,按下,松开
16 };
17
18
19 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
20 {
21 struct key_event event;
22 int fd;
23 fd = open("/dev/key0", O_RDWR);
24 if(fd < 0)
25 {
26 perror("open");
27 exit(1);
28 }
29
30 while(1)
31 {
32 read(fd, &event, sizeof(struct key_event));
33
34 if(event.code == KEY_ENTER)
35 {
36 if(event.value)
37 {
38 printf("APP__ key enter down\n");
39 }else{
40
41 printf("APP__ key enter up\n");
42 }
43 }
44 }
45
46 close(fd);
47
48 return 0;
49 }
key_test.c登录后复制key_test.c1 ROOTFS_DIR = /home/linux/source/rootfs#根文件系统路径 2 3 APP_NAME = key_test 4 MODULE_NAME = key_drv 5 6 CROSS_COMPILE = /home/linux/toolchains/gcc-4.6.4/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi- 7 CC = $(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc 8 9 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) 10 11 KERNEL_DIR = /home/linux/kernel/linux-3.14-fs4412 #编译过的内核源码的路径 12 CUR_DIR = $(shell pwd) #当前路径 13 14 all: 15 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) modules #把当前路径编成modules 16 $(CC) $(APP_NAME).c -o $(APP_NAME) 17 @#make -C 进入到内核路径 18 @#M 指定当前路径(模块位置) 19 20 clean: 21 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) clean 22 23 install: 24 sudo cp -raf *.ko $(APP_NAME) $(ROOTFS_DIR)/drv_module #把当前的所有.ko文件考到根文件系统的drv_module目录 25 26 else 27 28 obj-m += $(MODULE_NAME).o #指定内核要把哪个文件编译成ko 29 30 endif Makefile登录后复制Makefile
执行用户程序,按下按键可以看到信息
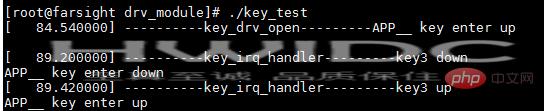
退出用户程序,按下按键,也会打印相应信息。

查看设备与中断节点信息:
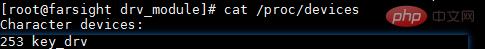

再看下CPU情况:
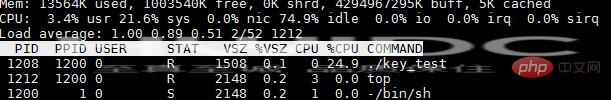
可以看到key_test应用程序占了很高的CPU,什么原因呢?
在应用程序中,是通过while循环,一直read内核的信息,当有按键中断发生的时候,就会对key_event赋值,在while循环里判断,进而打印出来,这样在用户空间与内核空间一直来回切换,一直read会十分消耗CPU资源。
解决思路:当有中断发生时,才来调用read,没有数据产生,跳出进程调度,进程休眠。
推荐学习:《linux视频教程》
以上就是linux 中断号是什么意思的详细内容,更多请关注海外IDC网其它相关文章!
【文章原创作者:美国服务器 https://www.68idc.cn处的文章,转载请说明出处】